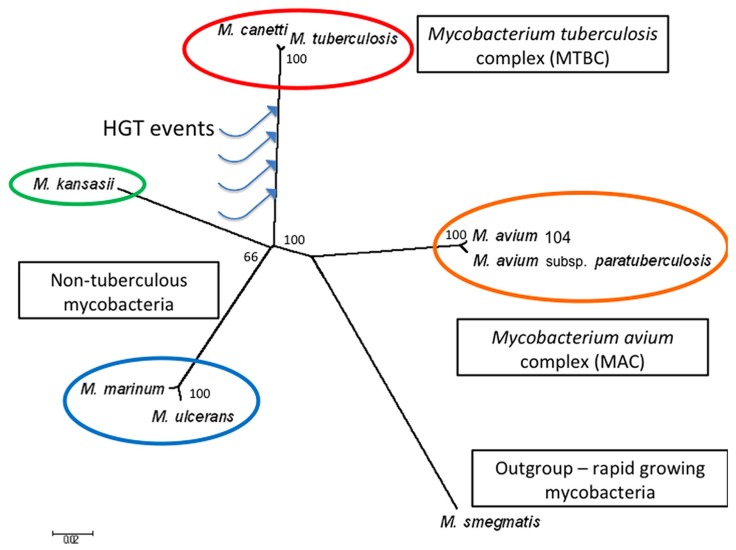
FIGURE 1.
Phylogeny of M. tuberculosis and closely related Mycobacterium species. The un-rooted phylogenetic tree was generated by MEGA6.0 using 20 randomly selected genes conserved across eight Mycobacterium species (Schwab et al., 2009). The blue arrows schematically represent where putative HGT events may have occurred, resulting in M. tuberculosis-specific genomic islands. The scale bar indicates 0.02 substitutions per nucleotide position, and the bootstrap values calculated using the neighbor-joining method (expressed as a percentage of 1000 replicates) are shown at the branch points. The fast growing species M. smegmatis is used as the out-group. Genes used are listed below (represented as M. tuberculosis genes): Rv0001-dnaA, Rv0041-leuS, Rv0236A–Rv0236A, Rv0248c–Rv0248c, Rv0285-PE5, Rv0287-esxG, Rv0288-esxH, Rv1085c–Rv1085c, Rv0197–Rv0197, Rv1304-atpB, Rv1305-atpE, Rv1894c–Rv1894c, Rv2172c–Rv2172c, Rv2392-cysH, Rv2440c-obg, Rv2477c–Rv2477c, Rv3019c-esxR, Rv3045-adhC, Rv3392c-cmaA1, Rv3502c- hsd4A.