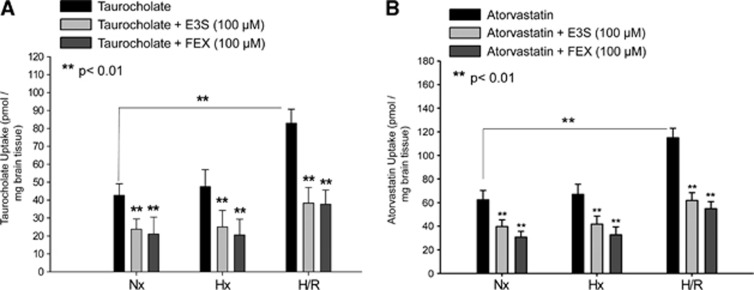
Figure 3.
Increased brain uptake of organic anion transporting polypeptide (Oatp) substrates after hypoxia/reoxygenation (H/R). Uptake of taurocholate (A) and atorvastatin (B) is increased in rat brain after H/R as determined by in situ brain perfusion. Animals were perfused with [3H]taurocholic acid (1.0 μCi/mL) or [3H]atorvastatin (0.5 μCi/mL) for 10 minutes in the presence and absence of Oatp inhibitors (E3S=estrone-3-sulfate; FEX=fexofenadine) (H=6% O2 for 1 hour and R=21% O2 for 10 minutes). Perfusions including Oatp1a4 inhibitors (i.e., 100 μmol/L E3S and 100 μmol/L FEX) were done 10 minutes before perfusion with [3H]taurocholic acid or [3H]atorvastatin. Animals were then perfused with [3H]taurocholic acid (1.0 μCi/mL; 10 mmol/L total concentration) or [3H]atorvastatin (0.5 μCi/mL; 0.013 μmol/L total concentration). Nx=Normoxia; Hx=Hypoxia. Results are expressed as mean±s.d. of six animals per treatment group. Asterisks represent data points that are significantly different from control.