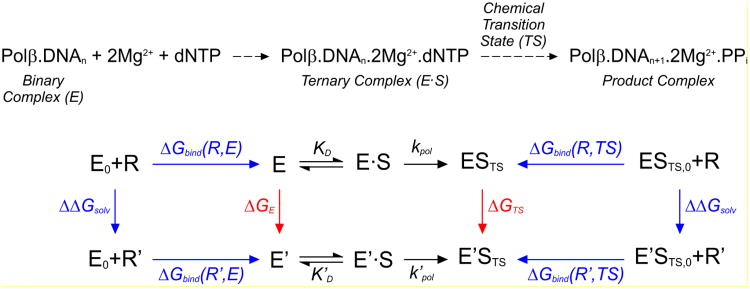
Figure 2.
Reaction scheme of the nucleotidyl transfer reaction catalyzed by Pol β (top) and thermodynamic cycle (bottom) for calculating the relative catalytic efficiency, Ω = (kpol/KD)'/(kpol/KD), of a mutant enzyme (see eq 1 to 5). States E0 + R and E0 + R′ correspond to an enzyme that lacks the side-chain of the mutated amino acid residue, and this side-chain (R for WT residue and R′ for the mutant), respectively, each individually solvated in aqueous solution. States E and E′ denote WT and mutant enzymes in aqueous solution, respectively (i.e., for Pol β, E0, E and E′ denote Pol β complex with bound primer-template DNA). States E·S and E′·S correspond, respectively, to WT and mutant enzymes containing a bound substrate (dNTP for Pol β). These enzyme-substrate complexes assume the geometry of the rate-limiting transition state in the states ESTS and E′STS. States ESTS, 0 + R and E′STS,0 + R′ correspond to the side-chain and enzyme-substrate transition states (in which the enzyme lacks the side-chain of the mutated amino acid residue), respectively, each individually solvated in aqueous solution. The free energies evaluated in FEP and LIE calculations are shown in green and blue, respectively.