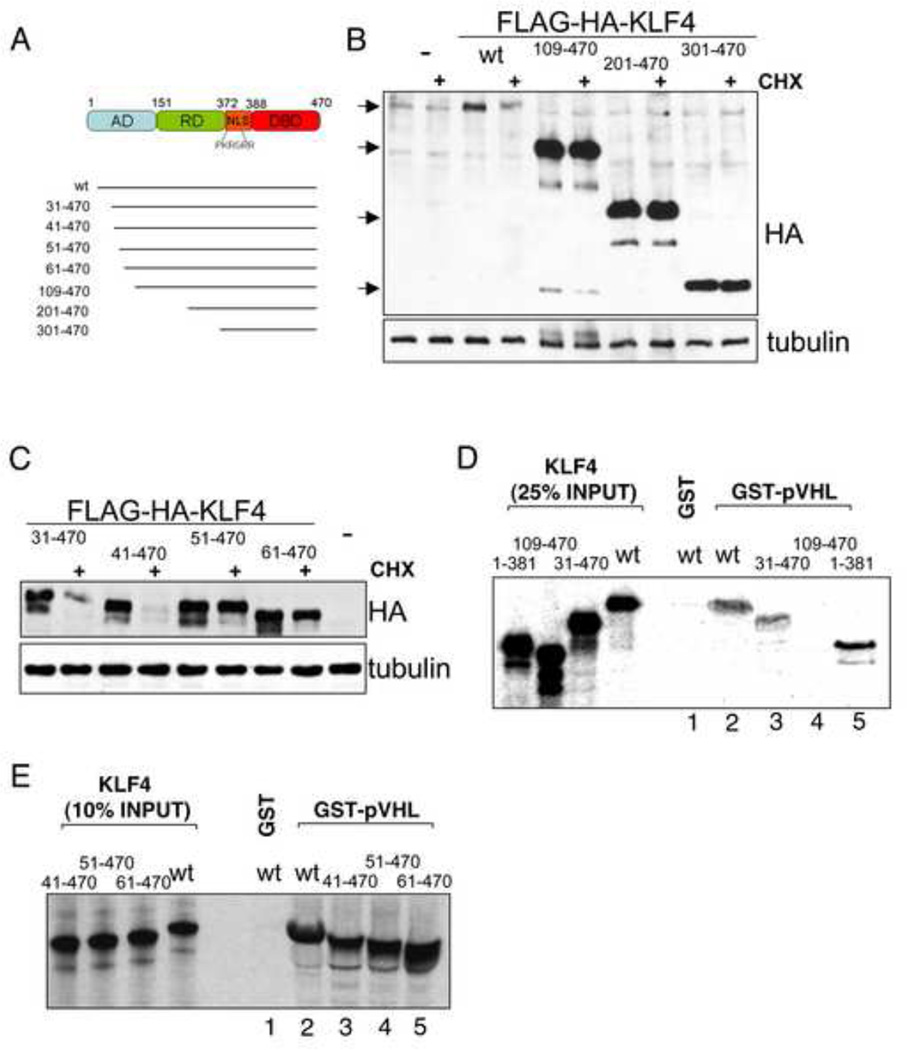
Figure 4. The KLF4 amino-terminus is important for degradation and interaction with pVHL.
(A) Schematic of human KLF4 with previously identified domains as well as deletion mutants used in the present study. AD, activation domain. RD, repression domain. NLS, nuclear localization signal. DBD, DNA-binding domain. (B) Deletion of KLF4 amino acids 1–108 stabilizes KLF4. Vectors for FLAG-HA-tagged wild type (wt) or deletion mutants of KLF4 were transfected into U2OS. 2 days after transfection cells were mock or cycloheximide (CHX) treated for 6 hours. Equal protein amounts of whole cell lysates were probed for KLF4 mutant levels by immunoblot with an antibody against the hemagglutinin (HA) tag. (C) Fine mapping of the amino-terminal KLF4 region required for degradation. The indicated deletion mutants were tested like in B. (D, E) An amino-terminal region of KLF4 is required for its interaction with KLF4. Beads with GST alone or GST-fused pVHL were incubated with various in vitro translated deletion mutants of KLF4 and bound proteins were analyzed by SDS-PAGE plus autoradiography. Deletion of amino acids 41–50 that stabilize KLF4 (C) does not affect pVHL binding (E).