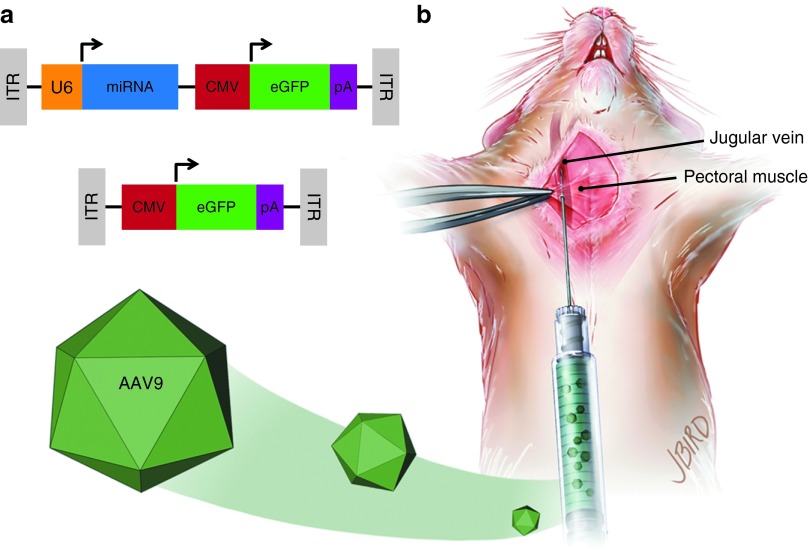
Figure 1.
Adeno-associated viral vector serotype 9 (AAV9) design and delivery. (a) Wild-type (WT) and Huntington's disease transgenic mice were injected with AAV9 containing either a bicistronic construct including a U6-driven micro RNA (miRNA) (either mi2.1 or miSCM) and a cytomegalovirus (CMV)-driven enhanced green fluorescent protein (eGFP) reporter gene (top) or a monocistronic construct consisting of a CMV-driven eGFP (bottom). miRNA constructs consisted of mi2.1, a human mutant HTT-specific miRNA, and miSCM, a control miRNA. (b) Mice were anesthetized and placed in a recumbent position, and a small incision was made lateral to the ventral midline, from the pectoral muscle to the lower neck. The jugular vein was exposed with blunt dissection. Viral vectors, saline, and/or 25% mannitol were delivered into systemic circulation through a direct injection into the jugular vein. Intrajugular injections were made using a 30-gauge needle after passing through the pectoral muscle. ITR, inverted terminal repeat. pA, poly-A tail.