Figure 2.
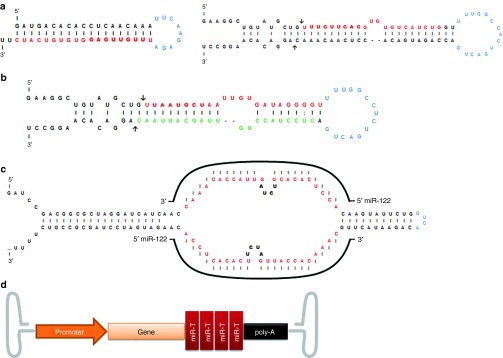
RNAi tools that can be expressed from an adeno-associated vectors (AAV): main features and structure. (a) Structure of shRNAs and artificial miRNAs. The mature shRNA or miRNA guide strand is represented in red with the seed sequence in bold. The loop is represented in blue, in the miRNA the arrows mark the Drosha cleavage sites, adapted from Borel et al., 2011.31 (b) Representation of the endogenous mouse miR-122, where mature miRNA-122-5p is represented in red with the seed sequence in bold, and the mature miRNA-122-3p is represented in green; the arrows mark the Drosha cleavage sites. (Note in this case the guide strand is in 5p and the passenger strand is in 3p, depending on the thermostability of the strands this can be reversed in other miRNAs.) (c) Representative sequence and structure of a miRNA tough decoy (TuD). In red is the sequence that is complementary to the target miRNA (e.g., miR-122) adapted from Xie et al., 2012.52 (d) Illustration of a vector construct with four copies of target sequence for miR-142 at the 3′UTR of the cDNA, adapted from Brown et al., 2006.62
