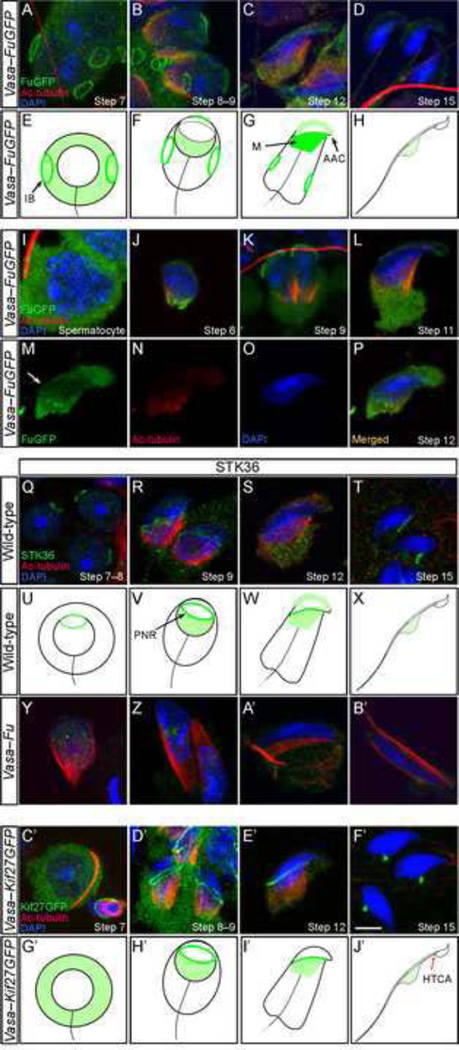
Figure 4. FuGFP and Kif27GFP localize to various microtubule-organizing centers of the developing sperm.
(A–D, I–P) Confocal immunofluorescence of testicular cells derived from Vasa-FuGFP transgenic mice where a Fu-GFP fusion protein was expressed under the germ cell-specific Vasa promoter. Cells were stained with antibodies against GFP (green) and acetylated tubulin (red) while the nucleus was stained with DAPI (blue). FuGFP was seen in the intercellular bridges (A) on the plasma membrane of round spermatids. The signal in the intercellular bridges persisted through the elongation steps of spermiogenesis. In spermatids with condensing chromatin (B, C), FuGFP was found in the manchette, the perinuclear ring and the acrosome-acroplaxome. In elongated spermatids (D), the manchette disappeared and the FuGFP signal was reduced. (E–H) Schematic diagram illustrating the localization of FuGFP (green) during spermiogenesis. (I–L) Additional stages of Vasa-FuGFP during spermiogenesis. Spermatocytes had broad cytoplasmic FuGFP staining (I). FuGFP staining was present in the manchette of a round spermatid (J) and in the developing acrosome-acroplaxome (J–L). (M–P) A step 12/13 elongating Vasa-FuGFP spermatid displayed immunofluorescence in the acrosome-acroplaxome, perinuclear ring (arrow) and manchette. (Q–T) Confocal immunofluorescence of testicular cells derived from wild-type adult mice. Cells were stained with antibodies against STK36 (green) and acetylated (Ac) tubulin (red); the nucleus was stained with DAPI (blue). STK36 signal was primarily detected in the perinuclear ring of round (Q), elongating (R, S) and elongated (T) spermatids. Weaker STK36 staining was also present in the manchette and the acrosome-acroplaxome (S). (U–X) Schematic diagram illustrating the localization of endogenous Fu (Stk36) during spermiogenesis. Not drawn to scale. (Y–B’) Confocal immunofluorescence of testicular cells derived from Vasa-Fu adult mice. STK36 staining was residual and non-specific. (C’–F’) Confocal immunofluorescence of testicular cells derived from Vasa-Kif27GFP transgenic mice. GFP signal was detected in the cytoplasm of round spermatids (C’). In elongating spermatids (D’, E’), specific signal was detected in the manchette and along the perinuclear ring that borders it. Kif27GFP signal translocated to the head-tail coupling apparatus (HTCA) at later stages (F’). After spermiation, no GFP signal was detected in the spermatozoa for either FuGFP or Kif27GFP. Scale = 5 µm for A–D, I–T, Y–B’. (G’–J’) Schematic diagram illustrating the localization of Kif27GFP (green) during spermiogenesis. Not drawn to scale. IB, intercellular bridge; M, manchette; AAC, acrosome-acroplaxome complex, PNC, perinuclear ring, HTCA, head-tail coupling apparatus.