Figure 6.
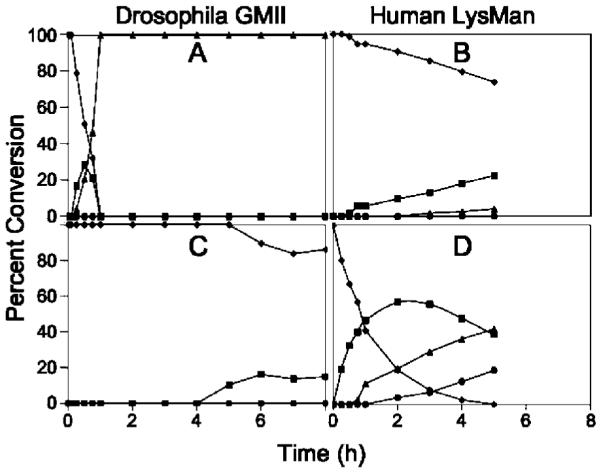
In Vitro digestion time course of Man5GlcNAc2-PA and GlcNAcMan5GlcNAc2-PA by dGMII and hLM. Purified recombinant dGMII (A, C) and hLM (B, D) were used in digestion time course studies with GlcNAcMan5GlcNAc2-PA (A, B) or Man5GlcNAc2-PA (C, D) as substrates. Cleavage of the substrates (GlcNAcMan5GlcNAc2-PA or Man5GlcNAc2-PA, ◆) to smaller glycan structures (GlcNAcMan4GlcNAc2-PA or Man4GlcNAc3-PA, ■; GlcNAcMan3GlcNAc2-PA or Man3GlcNAc3-PA, ▴; GlcNAcMan2GlcNAc2-PA or Man2GlcNAc3-PA, ●) were quantitated by HPLC. dGMII cleaved GlcNAcMan5GlcNAc2-PA ~80-fold faster than Man5GlcNAc2-PA at equivalent enzyme concentrations. Minimal digestion of Man5GlcNAc2-PA or GlcNAcMan5GlcNAc2-PA by hLM was detected when equivalent enzyme activity units (based on 4MU-α-Man activity) of hLM and dGMII were employed (not shown). Increasing the enzyme concentration of hLM in the in vitro assays by 100-fold (B, D) resulted in detectable cleavage of Man5GlcNAc2-PA, but cleavage of GlcNAcMan5GlcNAc2-PA remained ~16-fold slower.
