Table III. Leaf and environmental parameter values used in the various solutions reported in the figures.
| Quantity | Symbol | Red Oak (Fig. 2) | Sunflower (Fig. 3) | Condensing Leaf (Fig. 4) | EFM Leaf (Fig. 5) | Unitsa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leaf thickness, adaxial | 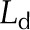 |
167.7 × 10−6 | 200 × 10−6 | 167.7 × 10−6 | 167.7 × 10−6 | m |
| Leaf thickness, abaxial | 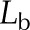 |
94.3 × 10−6 | 200 × 10−6 | 94.3 × 10−6 | 94.3 × 10−6 | m |
| Liquid area fraction, adaxial | 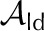 |
0.95 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | – |
| Liquid area fraction, abaxial | 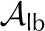 |
0.7 | 0.2 | 0.15 | 0.4 | – |
| Vapor area fraction, adaxial | 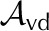 |
0.05 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | – |
| Vapor area fraction, abaxial | 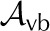 |
0.3 | 0.8 | 0.85 | 0.6 | – |
| Palisade absorbed radiation | 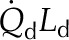 |
0.8 SR | 0.9 SR | 0.8 SR | 0.8 SR | J m−2 s−1 |
| Spongy absorbed radiation | 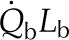 |
0.2 SR | 0.1 SR | 0.2 SR | 0.2 SR | J m−2 s−1 |
| Leaf hydraulic capacity | 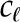 |
9.3 × 10−4 | – | – | – | mol m−3 Pa−1 |
| Vascular conductance | 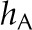 |
2.1 × 10−8 | 1 × 10−7 | 2.1 × 10−8 | 2.1 × 10−8 | mol m−2 Pa−1 s−1 |
| Vascular conductance scaling factor | 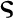 |
0.67 | – | – | 0.6 - 0.8 | – |
| Root and stem conductance | Krs | – | – | 6 × 10−9 | – | mol m−2 Pa−1 s−1 |
| Hydraulic conductivity cells | 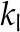 |
6.97 × 10−13 | 1 × 10−12 | 6.97 × 10−13 | 6.97 × 10−13 | mol m−1 Pa−1 s−1 |
| Thermal conductivity cells | 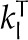 |
0.286 | 0.2 | 0.286 | 0.286 | J m−1 K−1 s−1 |
| Stomatal conductance, total | gs | 0.3 | 0.71 | 0.34 | 0.3 | mol m−2 s−1 |
| Characteristic leaf length | lc | 0.1 | – | 0.1 | 0.1 | m |
| Emissivity, long-wave, leaf |  |
0.96 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.96 | – |
| Boundary layer conductance (one side, cuvette) | gbl | 1.42 | 1.42 | – | – | mol m−2 s−1 |
| Wind speed | uw | 3.86 | – | 3.86 | 3.86 | m s−1 |
| Relative humidity | RH | 44% | 84% | 85% | 44% | – |
| Temperature, air (base) | Tair | 301.5 | 298.15 | 301.5 | 301.5 | K |
| Photosynthetic photon flux density | PPFD | 1,700 | – | 1,700 | 50–2,000 | μmol m−2 s−1 |
Dashes indicate a dimensionless (unitless) quantity.
