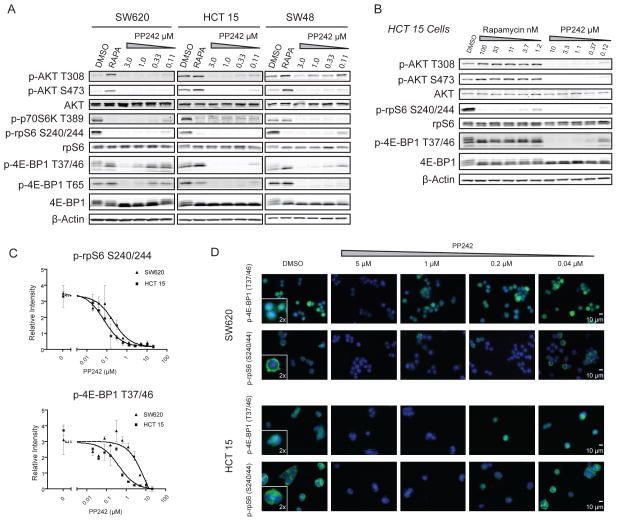
Figure 2.
mTORC1 substrates are differentially inhibited in PP242 resistant versus sensitive cell lines (A) 4E-BP1 is differentially inhibited in PP242 resistant and sensitive colon cancer cell lines. Representative cell lines SW620, HCT 15 and SW48 were treated with PP242 or rapamycin (20 nM) for 1 hour and analyzed by western blotting. (B) Differential inhibition is reminiscent of incomplete mTORC1 inhibition by rapamycin. In HCT 15 cells, rapamycin only partially inhibits 4E-BP1 phosphorylation after a 1 hour treatment, despite potently blocking rpS6 phosphorylation. (C) Quantification of mTORC1 substrate inhibition shows that inhibition of p-4E-BP1 and not inhibition of p-rpS6 tracks with growth inhibition. Quantification was performed on western blots of lysed cells after treatment for 1 hour with increasing PP242 concentrations in two independent experiments. (D) Immunofluorescence of mTORC1 substrates reveals consistent subcellular localization despite differential inhibition by PP242. SW620 and HCT 15 cells were treated with increasing concentrations of PP242 for 1 hour, formalin fixed and stained for either p-4E-BP1 or p-rpS6 (both green) and counterstained with DAPI (blue). PP242 treatment does not alter the subcellular localization of either phosphorylated substrate.