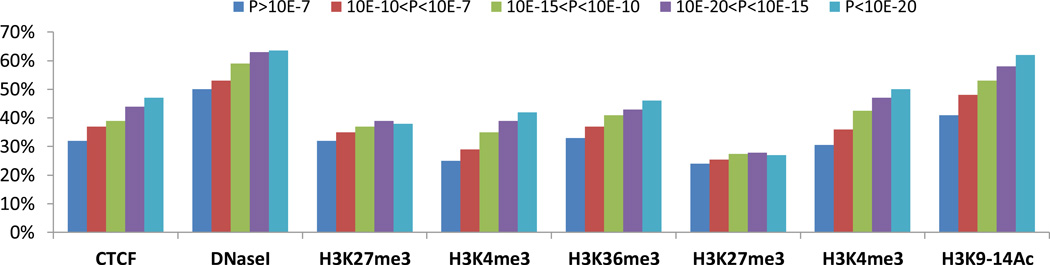
Figure 3. Chromatin marks are increasingly enriched on meQTL SNPs with larger effect sizes.
(a) We split cis-meQTL SNPs into five categories according to the meQTL association strength (P>10−7, 10−7>P>10−10, 10−10>P>10−15, 10−15>P>10−20, P<10−20). A SNP is determined to be related with a regulatory region if the SNP or any LD-related SNP (r2 ≥ 0.8) resides in the ChIP-Seq peaks of the regulatory regions. Regulatory elements include CTCF binding sites, DNaseI hypersensitive sites and histone marks from small airway epithelial cells (SAEC) from ENCODE and human alveolar epithelial cells (hAEC) from our laboratory. For each p-value category, we calculated the proportions of cis-meQTL SNPs related with regulatory regions. The figures show that the proportions of cis-meQTL SNPs related with regulatory regions increase with the significance of meQTL associations except for the repressive mark H3K27me3.