Figure 2.
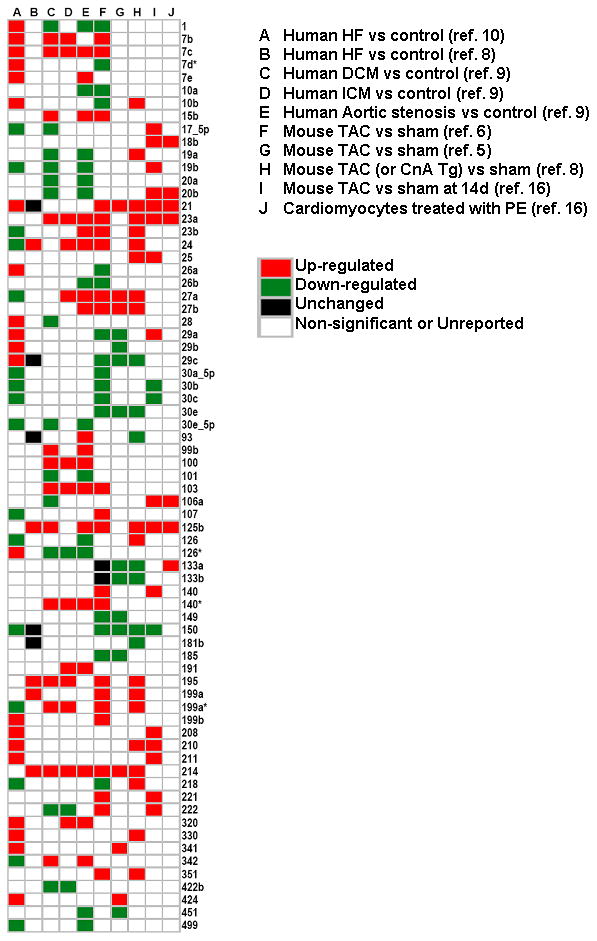
miRNA expression profiles in experimental models and human heart failure. A Pubmed search (May-June 2008) was conducted using the MeSH titles: ‘microRNA’, ‘heart disease’ and/or ‘heart failure.’ A total of 2314 articles were identified of which 614 review articles were excluded. The content of the 1696 original articles were reviewed for relevance with respect to the role of miRNAs in cardiac remodeling. Six studies reported global miRNA expression data (miRNA profiling) using micro-RNA micro-arrays, of which 3 evaluated miR expression in two or more experimental model systems.6, 7, 9–12 Differentially expressed miR candidates that were observed in at least two studies are graphically displayed with the relevant studies in columns and the accompanying changes in miRNA expression illustrated in rows. Red indicates miRs that were significantly up-regulated; green indicates miRs that were significantly down-regulated; black indicated no change in miR expression levels; white indicates miRs that were either unreported, equally expressed or not significantly different (p>0.05) between disease phenotype and controls.
