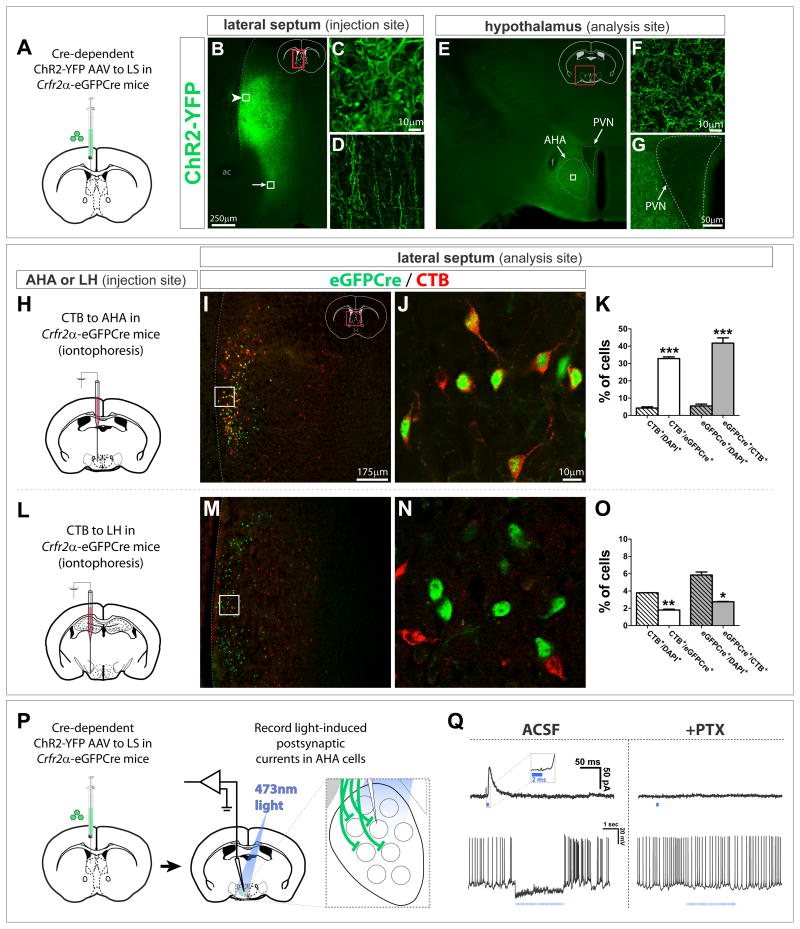
Figure 5. LS Crfr2α+ neurons make GABAergic synapses in the AHA.
(A–G) Cre-dependent ChR2-YFP AAV injected into Crfr2α-eGFPCre LS labeled cell bodies (arrowhead in B, enlarged in C) and axons (arrow in B, enlarged in D) Terminals were densest in AHA (E). All AHA labeling was axonal (F, enlarged from boxed area in E). YFP+ axons appeared to be excluded from the PVN (G). ac, anterior commissure; f, fornix; PVN, paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus.
(H–O) CTB retrograde tracing. eGFPCre (green) and CTB (red) in the LS of Crfr2α-eGFPCre mice that received iontophoretic injection of CTB into the AHA (I,J) or LH (M,N). (K) A significant fraction of Crfr2α+ neurons project to AHA (CTB+/DAPI+ = 4.3±0.7% vs. CTB+/eGFPCre+ = 33.0±1.0%, P<0.001), and Crfr2α+ neurons comprise a large fraction of the neurons that project to AHA from middle levels of LS (GFPCre+/DAPI+ = 5.5±1.1% vs. eGFPCre+/CTB+ = 42.0±3.1%, P<0.001). (O) Few Crfr2α+ neurons innervate the LH (CTB+/DAPI+ = 3.8±0.01% vs. CTB+/eGFPCre+ = 1.8±0.1%, P<0.01), with most projections to this region coming from Crfr2α− cells (GFPCre+/DAPI+ = 5.9±0.4% vs. eGFPCre+/CTB+ = 2.8±0.1%, P<0.05). Counts done at bregma+0.6 in LS regions that contained CTB+ cells. Total n = 7,737 DAPI+ cells (AHA) and n = 5,767 DAPI+ cells (LH). Values indicate mean±s.e.m.
(P,Q) CRACM in standard ACSF or plus 100μM picrotoxin (PTX). (Q) Single 2ms pulses of 473nm light evoked IPSCs blocked by PTX (top). Inset, higher temporal resolution to illustrate response latency. (bottom), picrotoxin-sensitive inhibition of spontaneous firing observed by presynaptic terminal photostimulation (15Hz, 2ms pulses).
See also Figure S5.