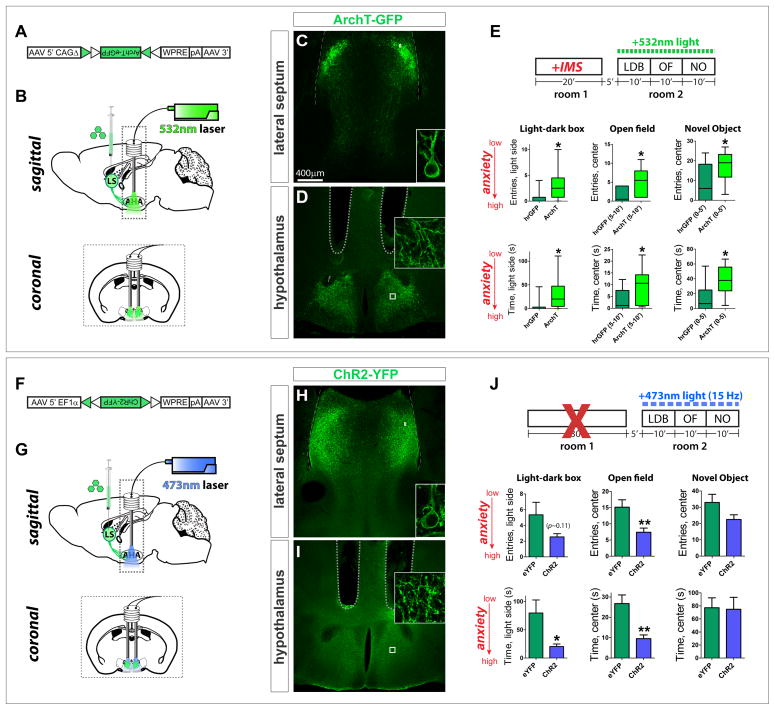
Figure 6. LS Crfr2α+ projections to AHA are necessary for stress-induced anxiety.
(A) Cre-dependent ArchT-GFP AAV.
(B–E) Axon terminal inhibition. (C,D) ArchT-GFP in LS Crfr2α+ (C) cell bodies and (D) and axons in AHA. (E) Photoinhibition of Crfr2α+ axon terminals in AHA during behavioral testing in IMS-stressed mice reduces anxiety. hrGFP (n=10) vs. ArchT (n=12), data presented Mann-Whitney U value, P value: LDB, entries in light side (U = 25.0, P<0.05), time in light side (U = 24.0, P<0.05); OF(5–10′), entries in center (U = 21.5, P<0.05), time in center (U = 26.0, P<0.05); NO(0–5′), entries in center (U = 29.5, P<0.05), time in center (U = 19.0, P<0.05).
(F) Cre-dependent ChR2-YFP AAV.
(G–J) Axon terminal stimulation. (H,I) ChR2-YFP in LS Crfr2α+ (H) cell bodies and (I) axons. (J) Stimulation of Crfr2α+ axon terminals in AHA during testing increased anxiety. eYFP(n=17) vs. ChR2(n=15): LDB, entries in light side (5.2±1.6 vs. 2.5±0.4, P>0.1), time in light side (79.9±23.2 vs. 20.3±4.6, P<0.05); OF, entries in center (15.1±2.3 vs. 7.4±1.3, P<0.01), time in center (26.8±4.2 vs. 9.5±1.8, P<0.01); NO, entries in center (32.9±5.0 vs. 22.5±2.9, P=0.08), time in center (77.2±15.2 vs. 74.9±18.3, P>0.1); values indicate mean±s.e.m. P values represent two-tailed unpaired t-tests.
Dashed lines in (D,I) indicate guide tips.
See also Figure S6.