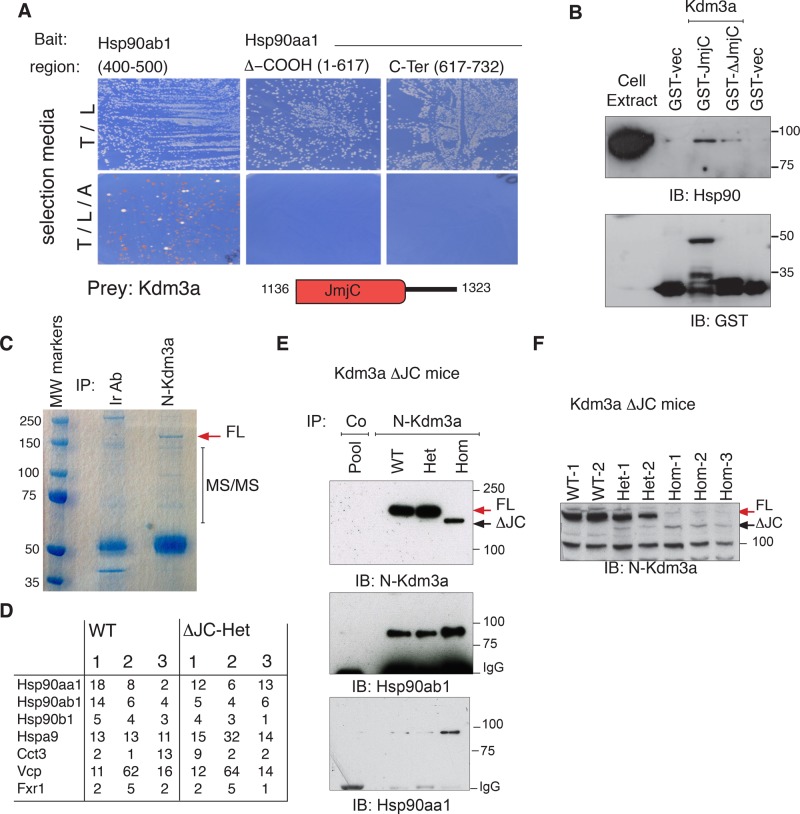
FIGURE 5:
Kdm3a interacts with Hsp90 and other cellular chaperones in vitro and in vivo. (A) Positive clones identified from a large two-hybrid screen using Hsp90 as baits were purified, retransformed into yeast, and mated to reassess interactions. The catalytic domain of Kdm3a can rescue amino acid deficiency of the parental yeast strain only when Hsp90ab1 is the bait. Diagram illustrates JmjC region contained in two-hybrid and GST constructs. (B) Bacterially expressed C-terminal end of Kdm3a-GST: GST-JmjC (aa 1136–1323), GST-ΔJmjC (aa 1283–1323), and GST vectors were incubated with HeLa cell extracts. Proteins bound to glutathione beads were resolved and blotted with the indicated antibodies to determine interactions of GST constructs with Hsp90. (C) TrueBlue stain of whole adult testis extracts immunopurified with Kdm3a or an irrelevant antibody used as control (Ir Ab). The gel section indicated was cut for mass spectrometry (MS). (D) Table shows the number of unique peptides identified with >99% confidence for three independent immunopurifications resolved as shown in (C) for each genotype. Only proteins shared by the six runs and not found in control samples are included. (E) An antibody directed to the N-terminal end of Kdm3a pulls down endogenous Hsp90 from testis. Note that the in-frame deletion Kdm3a protein encoded by the floxed Kdm3a allele still binds Hsp90aa1 and Hsp90ab1 strongly. (F) Total extracts from adult testis immunoblotted with Kdm3a show absence of full-length (FL) and low levels of truncated (ΔJC) Kdm3a protein in Kdm3aΔJC/ΔJC animals. Kdm3a-FL (red arrow) in wild-type (WT) and heterozygous (Het) but not control pool is indicated. 1–3 identify an animal for each genotype.