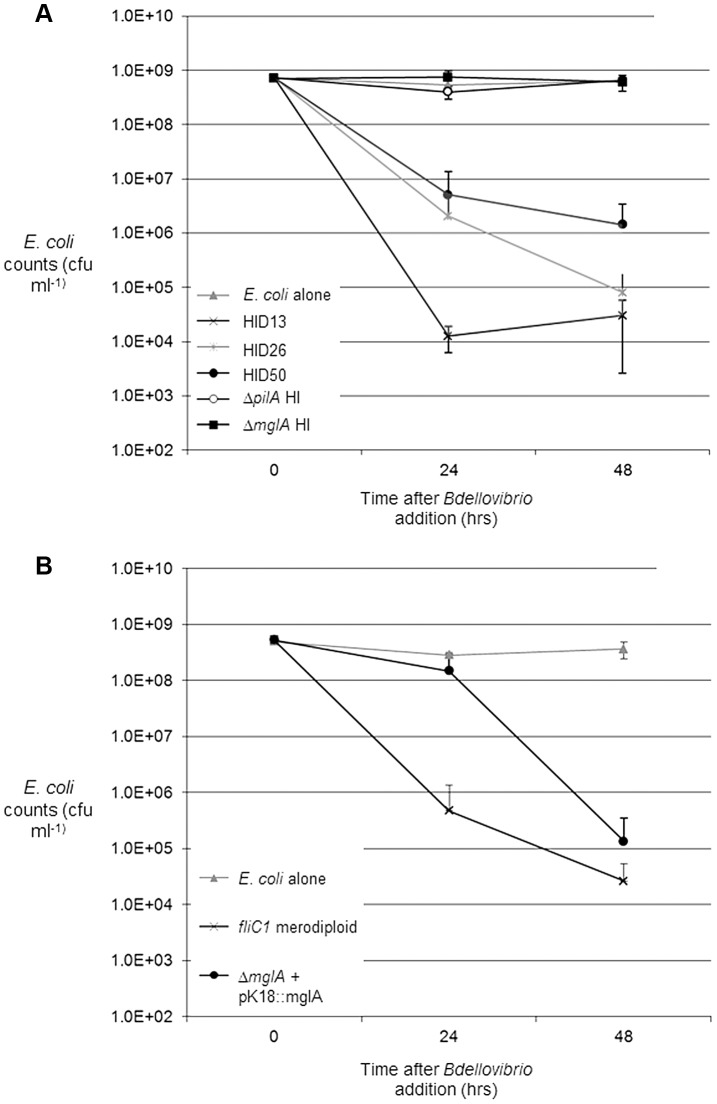
Figure 1. Predation and in cis complementation of B. bacteriovorus ΔmglA HI strains, on E. coli prey.
(A) Predation efficiency of the ΔmglA HI strain was assayed against predatory and non-predatory controls by the reduction of E. coli numbers over 48 hours. Three wild-type HI strains (HID13, HID26 and HID50) reduced E. coli numbers in liquid cultures by up to four logs (grey region shows known natural variation in predation rate between different wild-type HI isolates). The ΔmglA HI strain showed no reduction in E. coli numbers, comparable to a previously-studied, non-predatory ΔpilA HI strain, and to E. coli with no added B. bacteriovorus. (B) Reintroduction of the mglA ORF in cis to the ΔmglA HI strain in plasmid pK18::mglA restored predatory growth. Error bars represent 1 SD from the mean (for predation-testing of Δ bd2492 strain see Figure S5).