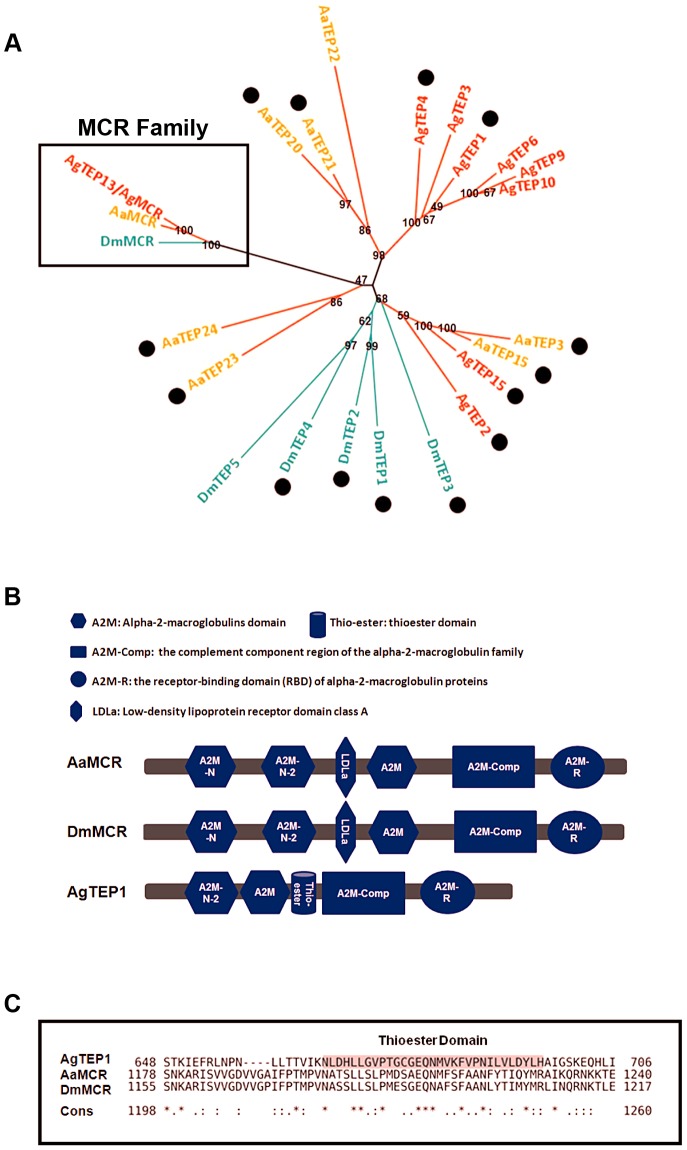
Figure 1. Comparison of the functional domains and phylogenetic analysis of insect thioester-containing proteins (iTEPs).
(A) Unrooted phylogenetic tree of iTEPs. The tree was constructed using the neighbour-joining (NJ) method based on the alignment of 23 iTEP protein sequences. The bootstrap values of 500 replicates (%) are indicated on the branch nodes. Anopheles gambiea (Ag), Aedes Aegypti (Aa) and Drosophila melanogaster (Dm) are indicated with red, yellow and green, respectively. Period represents the iTEPs with thioester domain. (B) Schematic representation of AaMCR, DmMCR and AgTEP1. The functional modules of MCRs and TEPs were predicted using the SMART (http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de/smart/set_mode.cgi?GENOMIC=1) and Pfam websites (http://pfam.sanger.ac.uk/). (C) Alignment of the sequence of thioester domain using CLUSTAL-X. The shadowed sequence is the predicted thoiester domain. Asterisk indicates the identical residues in all sequences of the alignment; colon indicates the conserved substitutions; period indicates the semi-conserved substitutions.