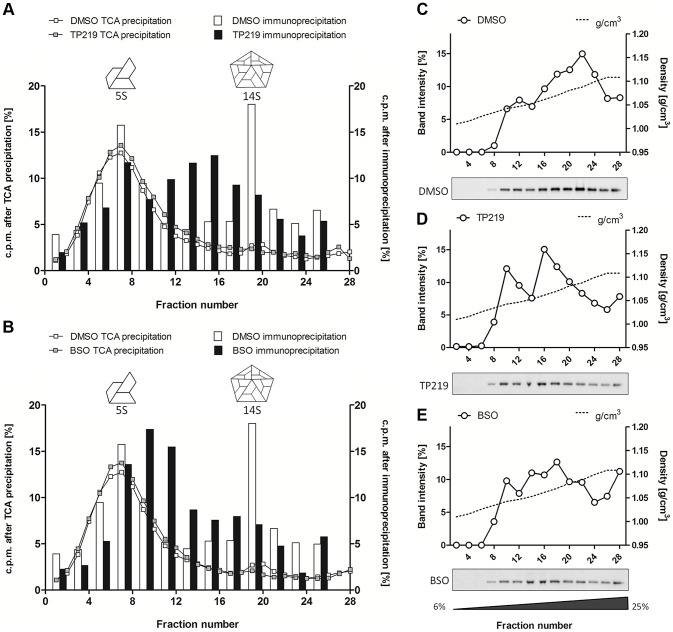
Figure 3. TP219- and BSO-treatment induces the formation of new assembly intermediates.
Effect of TP219-, BSO- and mock treatment on the levels of 5S protomers and 14S pentamers as determined by immunoprecipitation (A–B) and immunoblotting analysis (C–E). (A–B) Two consecutive fractions of a 6 to 25% gradient were pooled, immunoprecipitated using polyclonal anti-enterovirus antibodies and assayed for radioactivity. Different immunoprecipitated fractions (bars) are overlaid on TCA-precipitated fractions (lines) (derived from Figure 2) and the amount of radioactivity is expressed as % of total signal to normalize for the incorporation efficiency. Immunoprecipitated fractions of untreated cultures (A and B) are indicated in white; TP219- (A) or BSO- (B) treated cultures in black. Cartoon representations of the 5S and 14S assembly intermediates are indicated as well. (C–E) Two consecutive fractions of a 6 to 25% gradient were pooled, TCA-precipitated and subjected to Western blotting analysis using a monoclonal anti-VP1 antibody. Both the immunoblot (below) and quantification of the immunoblot (top) of mock (C), TP219- (D) and BSO- (E) treated cultures are depicted. Sucrose density is indicated as well and expressed as g/cm3.