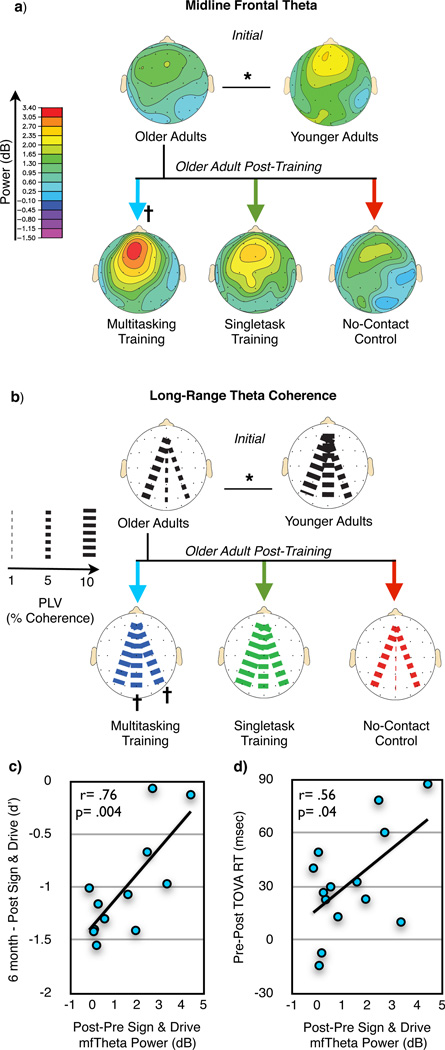
Figure 4.
Sign & Drive midline frontal theta activity and long-range theta coherence in younger adults and older adults Pre- and Post-training. a & b, For older adult training assessments, a group X session X condition ANOVA for each neural measure revealed significant interactions (in each case, F(2,41)> 4.98, p< .01, d> .93; see Supplemental Figure 6a & 6b), with follow-up analyses demonstrating improvement only for MTT during Sign & Drive (n= 15). For younger (n= 18) vs. older adult (n= 44) assessments, both neural measures revealed significant reductions in older adults (see Supplemental Figure 8a & 8b). c, Correlation in the MTT group between the change in midline frontal theta power and multitasking behavioral gain preservation 6 months later (n= 12). d, Correlation in the MTT group between the change in midline frontal theta power and behavioral improvement on the TOVA (n= 14).  = p< .05 within group improvement from Pre- to Post-Training, *= p< .05 between groups.
= p< .05 within group improvement from Pre- to Post-Training, *= p< .05 between groups.