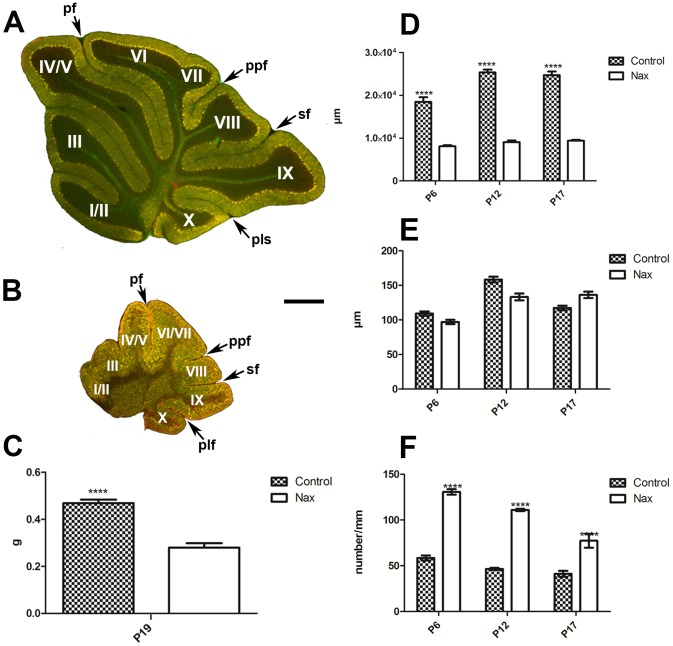
Figure 2. Sagittal sections through the nax mutant and wild type cerebella at P17 immunostained with CaBP and statistical graphs.
The lobules are indicated by Roman numerals. A) The cerebellum in the wild type developed normally with a lobulated vermis. B) The cerebellum in the nax mutant is smaller and underdeveloped, however the principal lobules in the vermis are present. C) Average brain weights (in grams (g) mean ± SEM) in the nax mutant and wild type at P19 indicate a significant decrease in weight of the nax brain. D) The rostrocaudal length of the nax mutant and wild type cerebellum at P6, P12, and P17, shows that the nax cerebellum is much smaller than the wild type. E) The Pcl/ml thickness in the nax mutant is smaller than that of the wild-type at P6 and P12, however it becomes larger at P17. F) The linear density of Pcs per 1 mm significantly decreases from P6 to P17 in the nax mutant, however it is higher than the linear density of Pcs in wild-type at every age. Scale bars: 500 um.