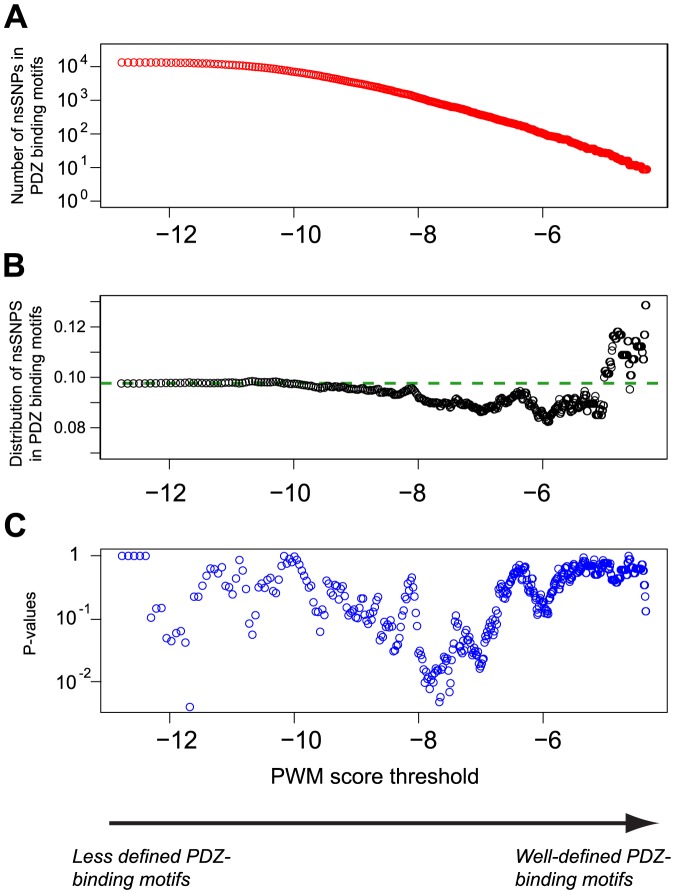
Figure 1. PDZ-binding linear motifs are affected by nsSNPs.
A) Number of nsSNPs that are found in PDZ-binding motif containing C-termini for a wide range of thresholds on PWM scores to define PDZ-binding motifs. Higher threshold values (corresponding to more stringent definitions of PDZ-binding motifs) result in few C-termini being considered as containing a PDZ-binding motif, hence few nsSNPs falling in these motifs. B) Distribution of nsSNPs in PDZ-binding motifs, computed as the ration between the number nsSNPs shown in panel A and the total number of amino acids in PDZ-binding motif containing C-termini. For the highest thresholds (>−6), the number of nsSNPs falling in PDZ-binding motifs is not lower than expected. Then for thresholds between −6 and −9, it becomes slightly lower. For even lower thresholds, we tend to the expected distribution observed for all C-termini (9.9% of positions affected by nsSNPs, dashed line). C) The corresponding P-value assuming a uniform distribution of nsSNPs in all C-terminal segments (binomial test).