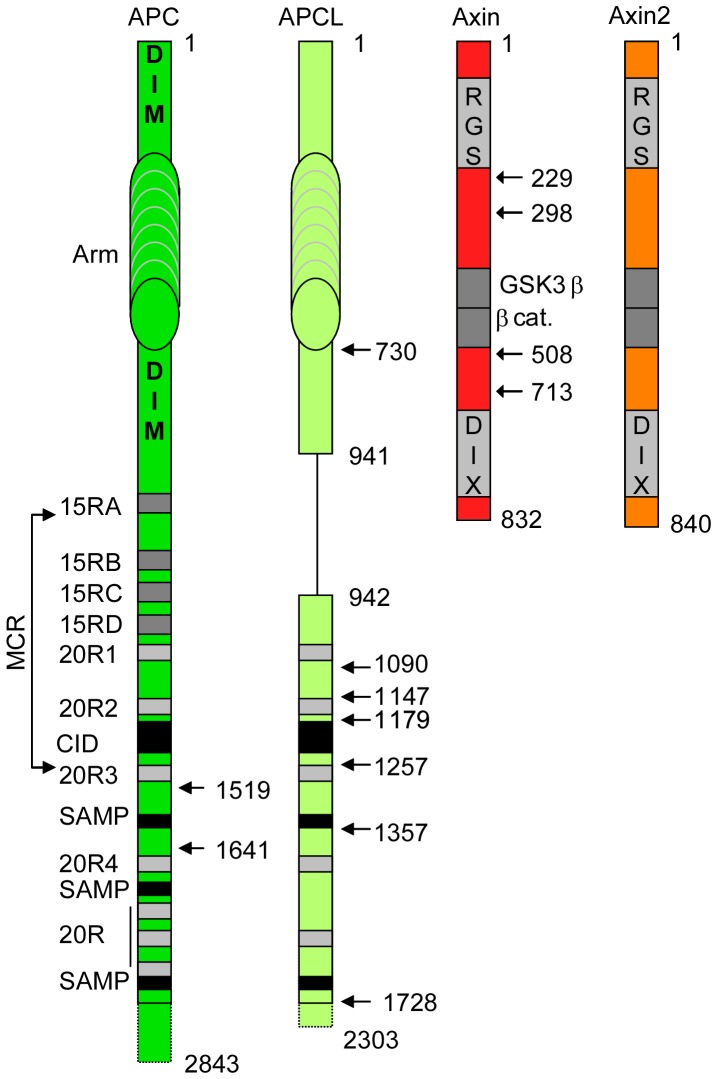
Figure 1. Schematic representation of human APC and APCL and rat Axin.
Functional modules are shown, including the two dimerisation domains of APC (DIM), the armadillo repeat domain (Arm), the 15 (15RA to D) and 20 (20R1 to 7) amino acid repeats that function as β-catenin binding sites, the β-catenin inhibitory domain (CiD) involved in β-catenin degradation and the SAMP repeats that represent Axin or Axin2 binding sites. The mutation cluster region (MCR) contains most of the APC truncating mutations that have been observed in colon cancer. The RGS (SAMP-binding region), DIX (oligomerisation), β-catenin and GSK3β domains in Axin are indicated. The numbers indicate the amino acid positions. The numbers with arrows correspond to the size of the different constructs analysed in this study, which were fused at the N-terminus to YFP (APC and APCL) or myc (Axin).