Figure 4.
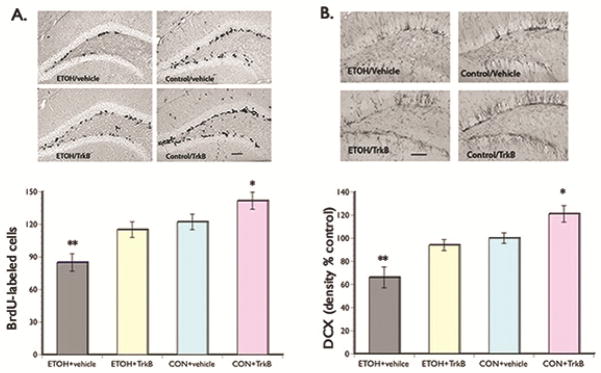
(A) BrdU Labeling. Upper panel: representative photomicrographs of BrdU staining scattered along both blades of the dentate gyrus. Lower panel: Bar graph shows significantly decreased survival of proliferating NPCs in the ETOH + vehicle group compared to the ETOH + TrkB and control rats. Overall, control rats that received the TrkB agonist showed the highest number of BrdU-labeled cells. These results suggest the role of BDNF in neuronal plasticity and its neuroprotective effects against the detrimental effects of alcohol. (B) DCX Labeling. Upper panel: representative photomicrographs of DCX staining in the dentate gyrus. Lower panel: Bar graph shows significantly decreased DCX immunoreactivity in the ETOH + vehicle group compared to the ETOH + TrkB and control rats. Control rats given the TrkB agonist showed the highest density of DCX staining. These results suggest the enhancing effects of BDNF signaling on the surviving newly formed cells to differentiate into neuronal phenotype. *p < 0.05; **p <0.01 (posthoc comparisons). Scale bar = 200 μm (left) and 100 μm (right).
