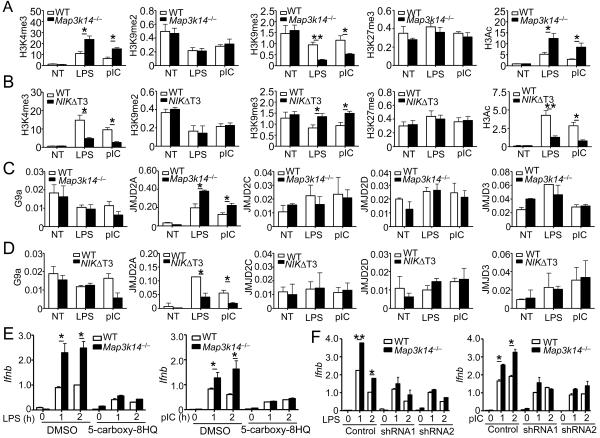
Figure 7. NIK regulates histone modifications and JMJD2A binding at the Ifnb promoter.
(A–D) BMDMs derived from Map3k14−/−, NIKΔT3 transgenic, or their WT control mice were stimulated with LPS or poly(I:C) for 1h. ChIP assays were performed to detect histone modifications (A and B) and binding of the indicated factors (C and D) at the Ifnb promoter. The Y axis is percentage (%) based on total H3 for A–B, and percentage (%) based on total input DNA for C–D. Data are representative of three independent experiments, and statistical analyses represent variations in technical replicates.
(E) WT and Map3k14−/− BMDMs were pretreated for 12 h with 20 mM of a JMJD2 inhibitor (5-carboxy-8HQ) and then stimulated with LPS or poly(I:C) as indicated. The relative amount of Ifnb mRNAs were quantified by QPCR and presented as fold relative to the internal Actb mRNA control.
(F) WT and Map3k14−/− BMDMs were infected with two different JMJD2A shRNAs or a non-silencing control shRNA and then stimulated with LPS and poly(I:C) as indicated. The relative amount of Ifnb mRNAs were quantified by QPCR and presented as fold relative to the internal Actb mRNA control. Data in all panels are representative of two-three independent experiments, and statistical analyses represent variations in technical replicates. *P<0.05 and **P<0.01. See also Figures S6 and S7