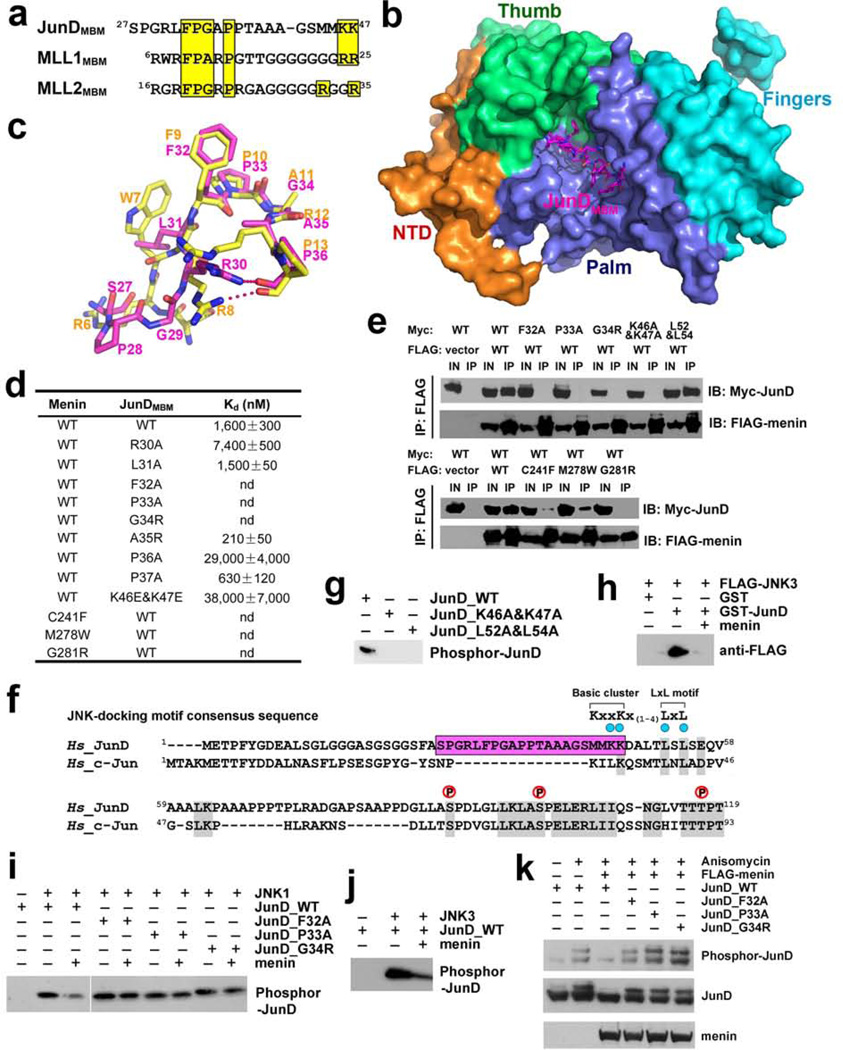
Figure 4. Menin binds to JunD and blocks JNK-mediated JunD phosphrylation.
a, Sequence alignment of the MBM sequences of JunD, MLL1, and MLL2. Conserved residues are highlighted in yellow. b, Crystal structure of the menin-JunDMBM complex. Menin is in surface representation and colored as in Fig. 1c. The JunDMBM peptide is in stick model and colored in magenta. c, Overlay of JunDMBM (magenta) and MLL1MBM (yellow). d, In vitro ITC data of wild-type and mutant menin-JunDMBM interactions (refer to Supplementary Fig. 10). e, Co-IP of the mutant menin-JunD interactions. Lanes marked “IN” represent 2.5% of input cell lysate used for the immunoprecipitation. f, Sequence alignment of JunD and c-Jun. The MBM sequence of JunD is highlighted in magenta. Key residues in the JNK-docking motif are denoted by blue dots and three phosphorylation sites are labeled above the sequence. The consensus sequence of the JNK-docking motif is shown at the upper-right corner. g, Lys46, Lys47, Leu52, and L54 in the JNK-docking motif are required for JunD phosphorylation by JNK. h, GST-pull down assay of FLAG-JNK3 by GST-JunD in the presence or absence of full-length menin. i, The phosphorylation of wild-type or mutant JunD by JNK1 was examined with in vitro kinase assay. The phosphorylated JunD was detected with anti-JunD phosphor-Ser100 antibody. j, The phosphorylation of JunD by JNK3 was examined as described in (i). k, HEK-293T cells were transfected with wild type or mutant c-Myc-JunD plasmids, either alone or together with FLAG-menin plasmids. Immunoblots were performed with either anti-phosphor-JunD (upper panel), anti c-Myc (middle panel) or anti FLAG (lower panel) antibodies to examine the phosphorylation level of JunD in response to anisomycin stimulation.