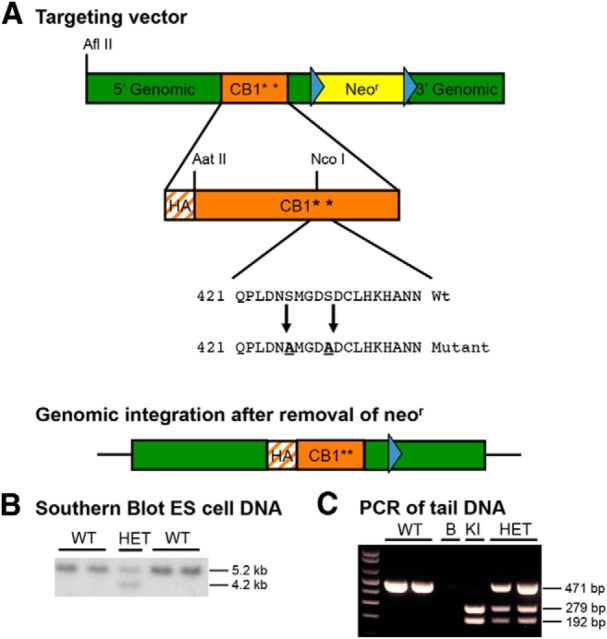
Figure 1.
Generation of S426A/S430A knock-in mice. A, Mice expressing a desensitization-resistant form of CB1R were produced using a targeting vector designed to mutate two putative GRK phosphorylation sites, serines 426 and 430, to nonphosphorylatable alanines. Additionally, the targeting vector introduced an N-terminal HA tag into CB1R and contained a NeoR gene flanked by FLP recombinase sites (blue triangles). B, Correct integration of the targeting vector was verified in ES cells by Southern blot analysis. A genomic DNA probe located outside of the targeting vector was used to detect a 5.2 kb WT fragment and a 4.2 kb mutant fragment after digestion of ES cell DNA with HindIII. C, PCR analysis of tail or ear DNA was used to determine the genotypes of offspring from heterozygous matings. NcoI digestion of the PCR of the mutant allele (KI) product produced two fragments, while the WT product produced a single band, and heterozygotes produced the predicted three bands. The no template control is shown in the lane labeled “B.”