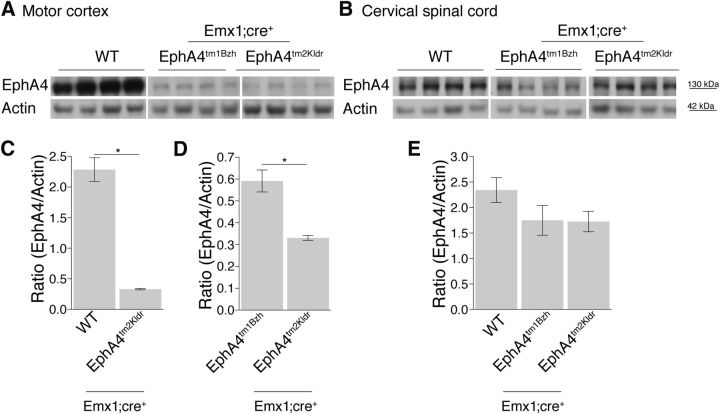
Figure 1.
Conditional elimination of EphA4 in the forebrain but not the cervical spinal cord. Immunoblotting analysis of motor cortex lysates shows decreased levels of EphA4 expression between wild-type and the two EphA4 conditional mutants (A), but minimal reductions in the cervical spinal cord (B). Lanes show data from individual mice (A, B). EphA4 was localized at 130 kDa and actin was localized between molecular weight markers at 55 and 35 kDa. Exposure times for gels were as follows: motor cortex EphA4, 20 s; actin, 6 s; cervical spinal cord, 60 s, actin, 6 s. C–E, Bars plot ratio of mean (±SE) EphA4 and Actin protein levels for each group (n = 4–5 mice/group). There is a significant reduction of EphA4 protein level in the motor cortex of homozygous Emx1-Cre;EphA4tm2Kldr compared with WT (C; p = 0.029, Mann–Whitney test). This reduction is more pronounced in the Emx1-Cre;EphA4tm2Kldr than the Emx1-Cre;EphA4tm1Bzh mutant (D; p = 0.028, Mann–Whitney test). Immunoblotting analysis from cervical spinal cord lysates showed similar protein level in wild-type and two EphA4 conditional mutants (p = 0.232, Kruskal–Wallis test, Dunn's posttest: p > 0.05; n = 4/group).