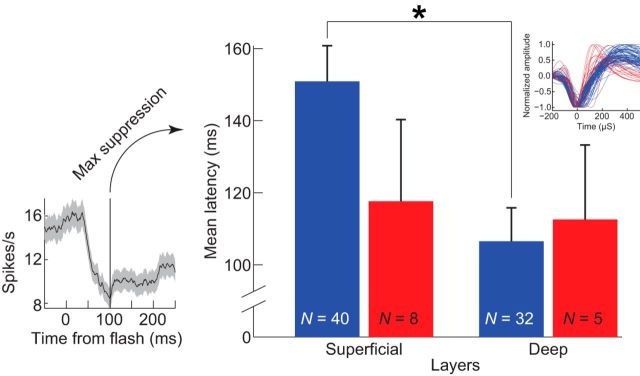
Figure 11.
Latency to maximum spike suppression differentiated by neuron depth and spike width. Superficial layers (II and III) versus deep layers (V and VI) and broad-spiking units (in blue) versus narrow-spiking units (in red). Error bars indicate SEM. Left, An example unit illustrating the measurement of latency to maximum spike suppression. Upper right inset shows the broad- and narrow-spiking units that make up the sample. A statistically significant difference was observed in the latency to maximum spike suppression between broad units recorded in superficial layers and broad units recorded in deep layers. No other comparisons differed significantly.