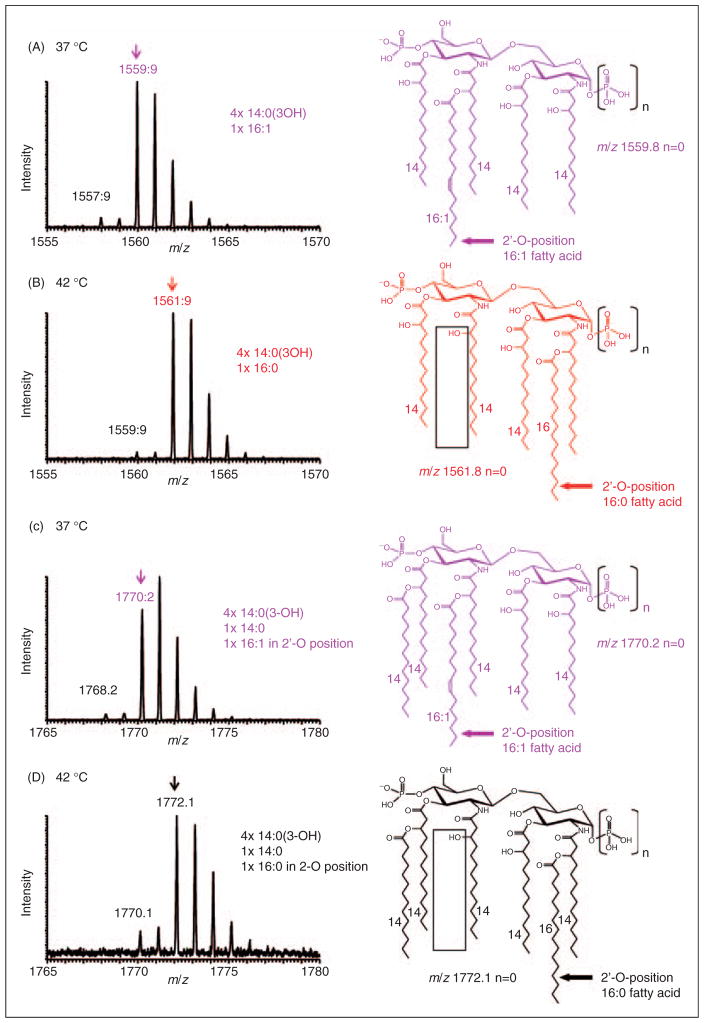
Figure 4.
Negative-ion MALDI–MS spectra of distinct lipid A species recorded at higher resolution in the UltraZoom mode. (A) E. coli lpxL strain MLK217 grown at 37°C showed an isotope pattern consistent with a monophosphoryl pentaacyl species at m/z 1559.9, which corresponds to an acyl composition of four 3-hydroxymyristic acids and 1 palmitoleic acid in the distal secondary 2′-O-position. (B) E. coli lpxL strain MLK217 grown at 42°C contains an isotope pattern for a pentaacyl species 2 u higher at m/z 1561.9, which corresponds to a fatty acid composition of four 3-hydroxymyristic acids and one palmitic acid at the proximal secondary 2-O-position. (C) and (D) show corresponding hexaacyl lipid A species at 37°C and 42°C, respectively (C) At 37°C the lpxL mutant hexaacyl lipid A with palmitoleic acid at the distal secondary 2′-O-position is a prominent species. (D) at 42°C different hexaacyl species with palmitic acid at the proximal secondary 2-O-position are produced. In all cases, the precise positions of the fatty acids shown in this figure were determined by MSn analysis, as described in the text and accompanying supplementary material.