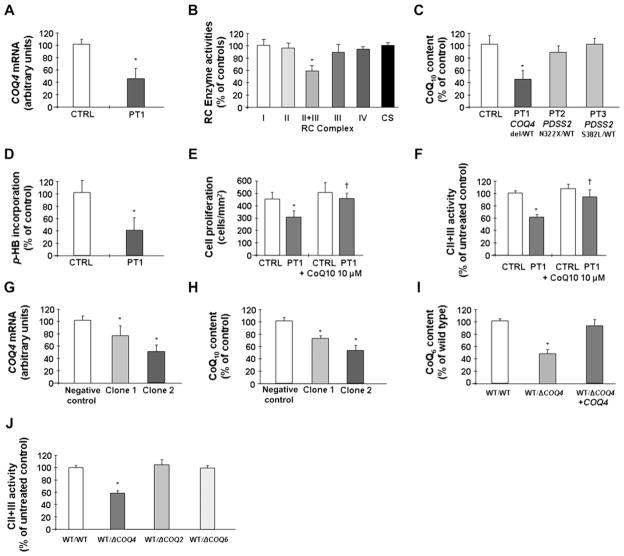
Figure 2.
(A) COQ4 mRNA expression and (B) respiratory chain enzyme activities, in PT1 cultured skin fibroblasts. (C) Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) content in PT1 cells and in cells of PT2 and PT3 who harbour heterozygous mutations in COQ1-PDSS2. (D) CoQ10 biosynthetic rate in PT1 cells measured by incorporation of 14C labelled p-HB. (E) Growth profile of PT1 skin fibroblasts. Incubation with 10 μM CoQ10 restores normal growth in patient cells. (F) Effect of CoQ10 supplementation on complex II+III activity in patient cells. (G) COQ4 mRNA levels and (H) CoQ10 levels in cells stably expressing an anti-COQ4 shRNA. (I) CoQ6 content in diploid yeast strains harbouring a heterozygous deletion of COQ4. Transformation with a plasmid-expressing COQ4 restores normal CoQ6 content in these cells. (J) Complex II+III activity in diploid yeast strains harbouring heterozygous deletions of COQ4, COQ2 and COQ6. Activities of other RC enzymes were normal (note that yeast does not have complex I). *Significant versus controls; †Significant versus untreated cells.