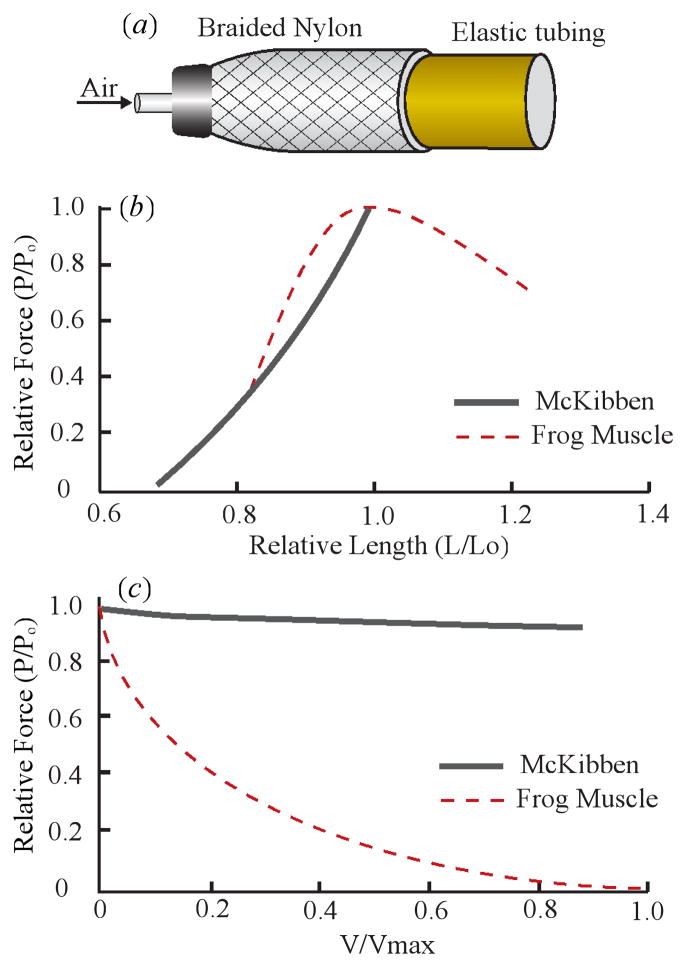
Figure 2.
Summary of key mechanical properties of McKibben actuators. (a) The McKibben type pneumatic actuator consisting of an internal elastic tube, surrounded by braided polyester. Inflation of the inner tubing causes shortening of the actuator along its long axis as well as the radial expansion of the actuator (b) The force-length relationship of a McKibben muscle (Klute et al. 2002) shown with the curve for a frog plantaris muscle (Azizi and Roberts, 2010). The McKibben actuator relationship shows an increase in force as length increases until it reaches its maximum length. (c) The Force-velocity relationship of the McKibben muscle (Klute et al. 2002) alongside the curve for the frog plantaris muscle (Azizi and Roberts, 2010). Unlike skeletal muscle, McKibben actuator shows little decrease in force as velocity increases.