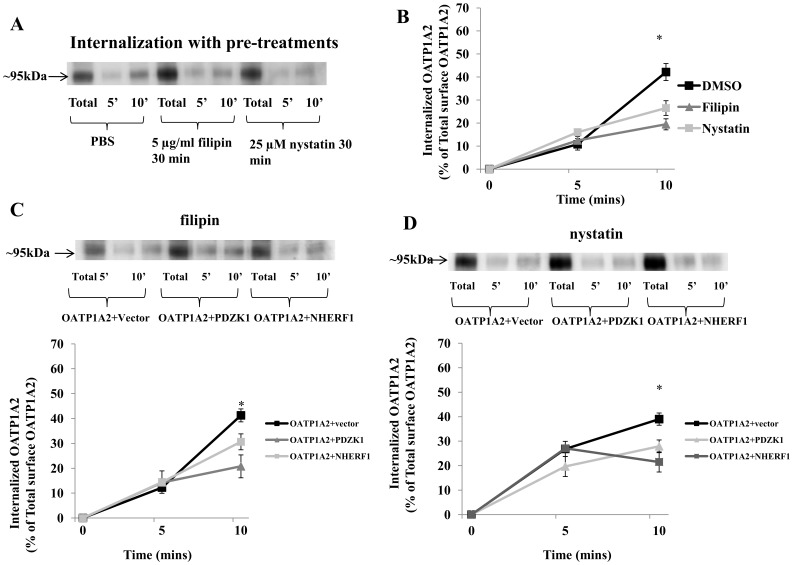
Figure 7. Caveolin-dependent internalization of OATP1A2 by PDZK1 and NHERF1.
(A) Disruption of the caveolin-dependent pathway impairs OATP1A2-N-flag internalization. HEK-293 cells over-expressing OATP1A2-N-flag were treated with filipin (5 µg/ml) or nystatin (25 µM) for 30 mins, relative to dimethylsulfoxide-treated control. The cells were allowed to internalize at 37°C for 5 or 10 mins as described under “Materials and Methods” followed by immunoblotting for OATP1A2-N-flag. (B) Internalized OATP1A2-N-flag as a percentage of the total initial pool of biotinylated OATP1A2-N-flag at the cell surface (means±S.E. of 3 individual experiments) *: Different from control: P<0.05. (C) Top panel: immunoblot analysis of OATP1A2-N-flag in HEK-293 cells containing co-expressed PDZK1-N-myc or NHERF1-N-myc after treatment with filipin (5 µg/ml) for 30 mins, followed by internalization at 37°C for 5 or 10 mins. Bottom panel: Internalized OATP1A2-N-flag as a percentage of the total initial pool of biotinylated OATP1A2-N-flag at the cell surface (means±S.E. of 3 individual experiments). *: Different from control: P<0.05 (D) Top panel: immunoblot analysis of OATP1A2-N-flag in HEK-293 cells containing co-expressed PDZK1-N-myc or NHERF1-N-myc after treatment with nystatin (25 µM) for 30 mins, followed by internalization at 37°C for 5 or 10 mins. Bottom panel: Internalized OATP1A2-N-flag as a percentage of the total initial pool of biotinylated OATP1A2-N-flag at the cell surface (means±S.E. of 3 individual experiments). *: Different from control: P<0.05. Blotting for β-actin in separate aliquots of total lysates was used to confirm uniform protein loading.