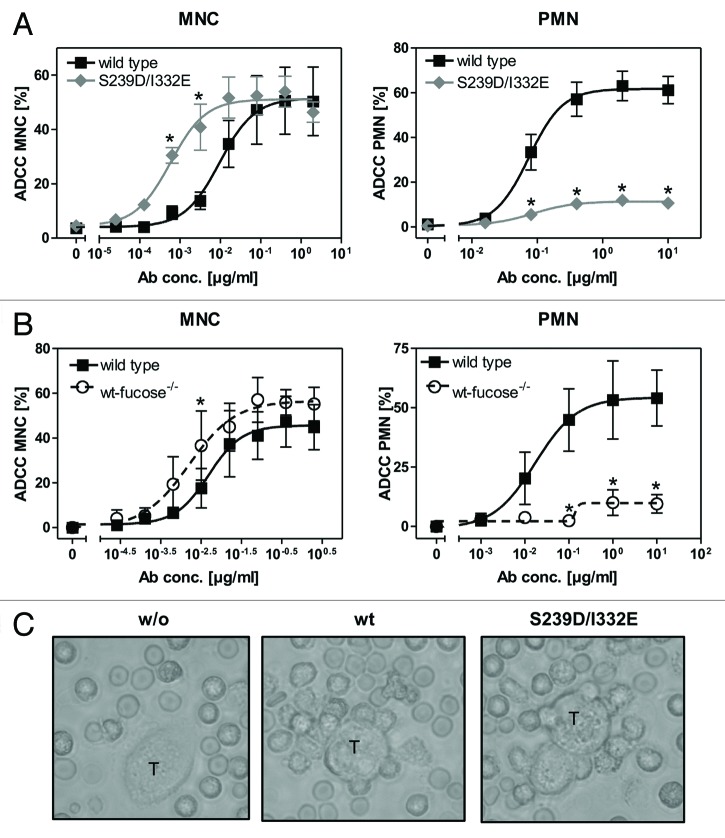
Figure 1. Glyco- or protein-engineered Fc variants optimized for FcγRIII binding mediated enhanced ADCC by MNC, but did not trigger PMN-mediated cytotoxicity. (A, B) ADCC against EGFR-expressing A431 cells was investigated in 3h 51chromium release assays in the presence of increasing concentrations of (A) protein-engineered or (B) glyco-engineered antibodies. ADCC by MNC was enhanced by protein- or glyco-engineered variants compared with wild type antibody (left panel). PMN triggered significant ADCC with wild type antibody, but were completely ineffective with both types of variants (right panel). Data are presented as mean ± SEM of at least three independent experiments with different donors. * P ≤ 0.05 for wild type vs. engineered antibodies. (C) FcγRIII-engineered antibody mediated tumor cell adhesion by PMN. A431 cell were co-incubated with GM-CSF stimulated PMN from healthy donors at an E:T ratio of 80:1 in the presence or absence of EGFR-targeted antibodies. After 3 h, microscopy was performed at 40x magnification (t = tumor target cells).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.