Figure 5. Pivotal role of activated Kupffer cells in the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and fibrogenesis.
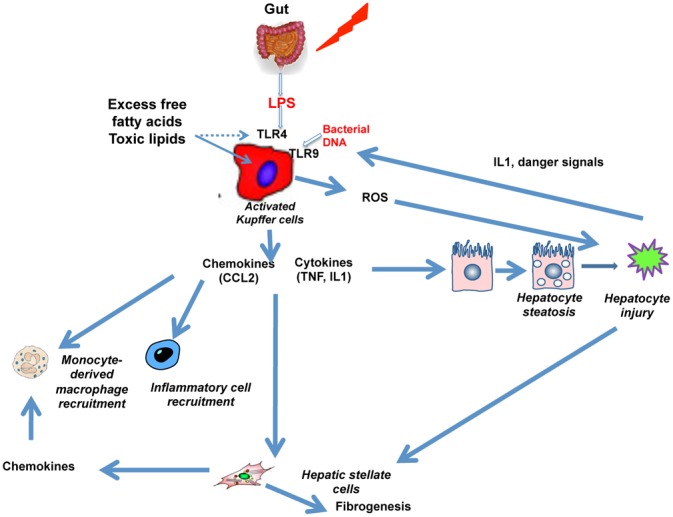
Increased levels of lipoipolysaccaride (LPS) and lipotoxic lipid products lead to activation of Kupffer cells, which release chemotactic factors (e.g. CCL2), and proinflammatory cytokines, and generate oxidative stress-related products including reactive oxygen species (ROS). These factors contribute to hepatocyte injury, which in turn, through danger signals, cause further activation of toll-like receptors (TLRs). In addition, inflammation and damage contribute to hepatic stellate cell activation and fibrosis.
