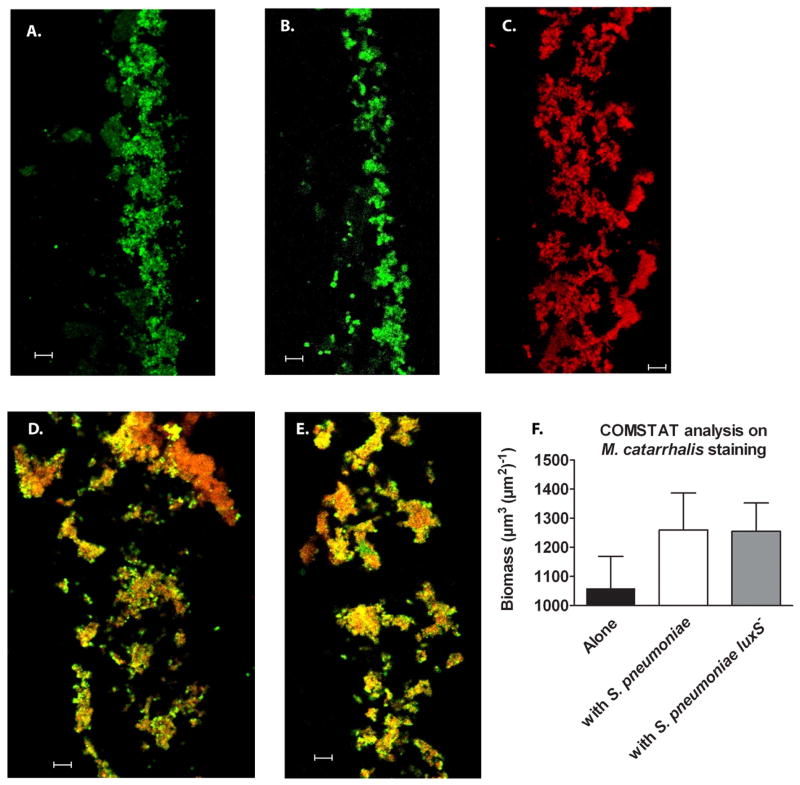
Figure 3. M. catarrhalis forms polymicrobial biofilms with S. pneumoniae in vitro.
S. pneumoniae EF3030 (green) and M. catarrhalis O35E (red) were seeded in 4 well Permanox chamber slides alone or together at 1:1,000 (as described in the methods section) and grown for 24 hours at 37°C. Biofilms were then fixed, frozen within OCT medium and cryosectioned (~5 μm/slice) and placed on slides. Bacteria were visualized using antibodies specific for pneumococi (rabbit anti-PspA) and Moraxella (monoclonal antibody 4G5), along with relevant fluorescent secondary antibody conjugates (Molecular Probes). Representative images of S. pneumoniae (A.), its luxS− mutant (B.), M. catarrhalis (C.), polymicrobial biofilms with S. pneumoniae and M. catarrhalis (D.), and polymicrobial biofilms with S. pneumoniae luxS− and M. catarrhalis (E.) were taken using CLSM. Images (n=5 frames per group) were analyzed by COMSTAT to determine biomass of M. catarrhalis (F.) alone or in polymicrobial biofilms. Scale bar = 10 μm.