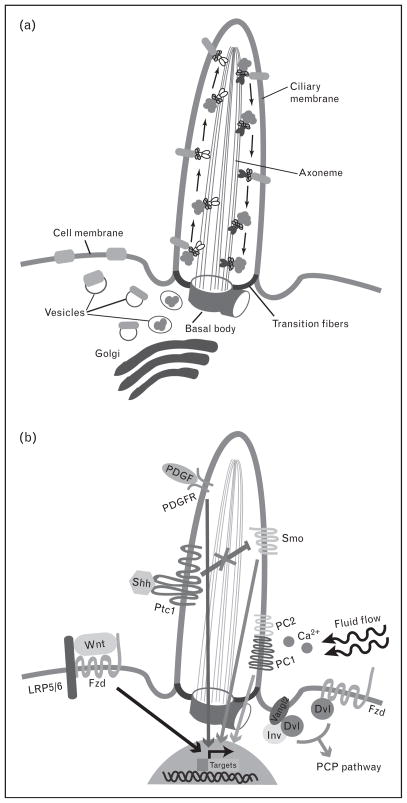
Figure 1. Intraflagellar transporting and signaling pathways within the primary cilium.
(a) The protein cargos are transported from the Golgi to the basal body by vesicle trafficking in the cellular cytoplasm. In order to move ciliary cytosolic and membrane proteins, kinesin 2 and dynein 2, motor proteins associating with intraflagellar transport (IFT) complex, travel along the axoneme between the base and the tip of the cilium in an anterograde and retrograde direction respectively. (b) The primary cilium modulates several signal transduction pathways. Sonic hedgehog (Shh) signaling is activated by binding of Shh to patched (Ptc1), releasing smoothened (Smo) and the downstream target gene transcription from inhibition. Canonical wingless (Wnt) signaling through low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein (LRP)5/6 and Frizzled (Fzd) is inhibited by the primary cilium, whereas noncanonical Wnt signaling [planar cell polarity (PCP) pathway] requires the primary cilium to be activated by Dishevelled (Dvl) interacting with either Fzd or Inversin (Inv)/other PCP components such as Vangl2. Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) signaling through PDGF receptor (PDGFR) requires ciliary localization of the receptor to activate downstream targets. In response to fluid flow, calcium signaling is activated through mechanosensing by polycystin-1 (PC1) and polycystin-2 (PC2) localized in the ciliary membrane.
 , ciliary membrane proteins;
, ciliary membrane proteins;
 , ciliary proteins;
, ciliary proteins;
 , IFT complex;
, IFT complex;
 , kinesin 2;
, kinesin 2;
 , dynein 2;
, dynein 2;
 , nonciliary proteins.
, nonciliary proteins.