Figure 2.
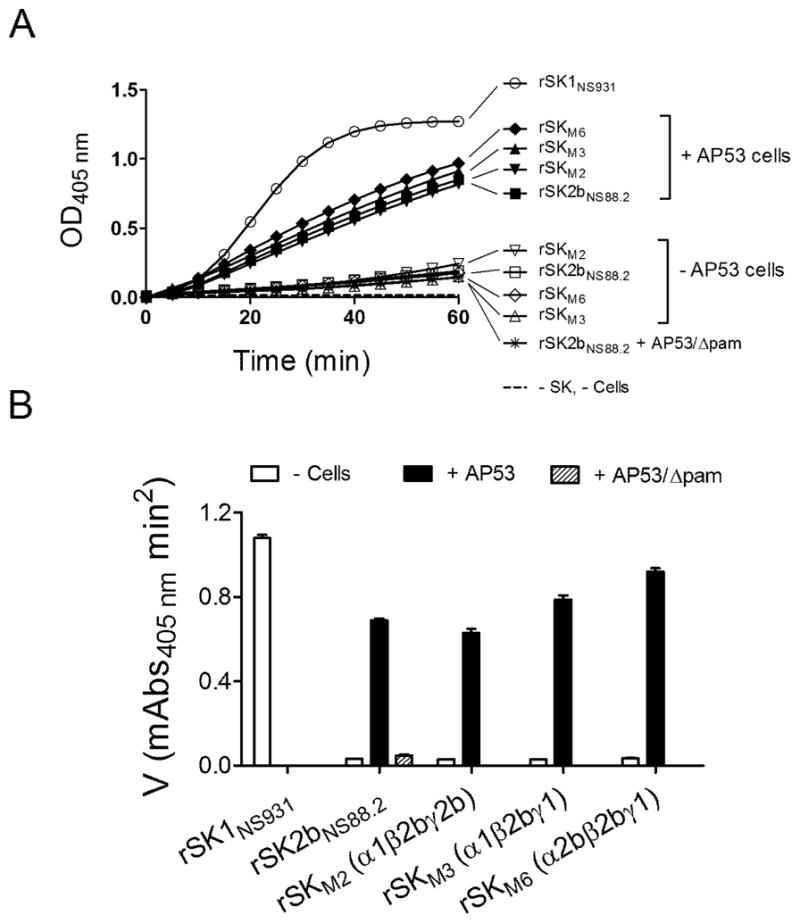
Activation of rhPg by purified rSK and rSK mutants in absence and in presence of GAS WT-AP53 cells or AP53/Δpam cells. (A). Activation of 200 nM of hPg by 5 nM (final concentrations) of purified rSKs, as labeled in Panel A. The unfilled symbols are assays absent cells, and the filled circles are assays in the presence of 20 μl of GAS WT-AP53 cells (A600 nm, 1.0). The control (dashed line) was performed under the same conditions, except without the addition of rSK and cells. The generation of amidolytic activity was monitored continuously by the absorbance at 405 nm (A405nm) versus time at 37 °C using 0.25 mM (final concentration) of S2251 as the hPm substrate. (B). The data from A were replotted as initial velocities of activation (as in Figure 1B).
