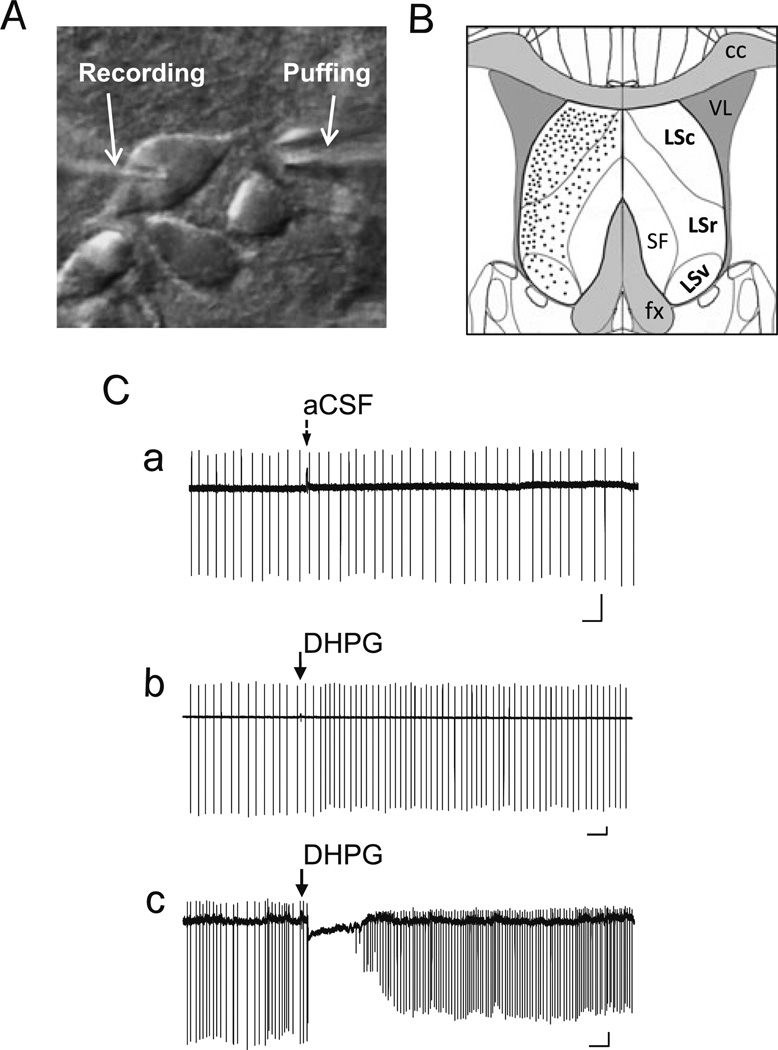
Fig. 1.
Pressure ejection of DHPG elicits two distinct response patterns of LS neuron firing in loose patch recordings. A, DIC image showing an LS neuron in brain slice held by a recording pipette and with an ejection electrode aimed at the dendrites near the soma. B, Diagram of coronal section of brain slice depicting the location and subdivisions of mouse lateral septal nucleus (LSc, LSr, and LSv). Black dots indicate the relative distribution of the LS neurons that were randomly picked for loose patch and whole-cell patch-clamp recordings in the current study. C, DHPG-evoked changes in firing patterns of LS neurons under loose-patch recordings. Loose patches were made using recording pipette filled with aCSF. Representative traces showing changes of firing activity elicited by ejecting aCSF (a) or 30 µM DHPG (b, c; 5–20 psi, 30 ms) onto wild-type (WT) LS neurons. Note aCSF ejection did not interfere with LS firing (Ca), but DHPG ejection onto LS neurons elicited either an increase in firing rate (Cb) or a momentary pause of firing followed by an increase in firing rate (Cc). Arrows indicate the time of ejection of aCSF or DHPG. Scale bars: 0.5 s, 50 pA