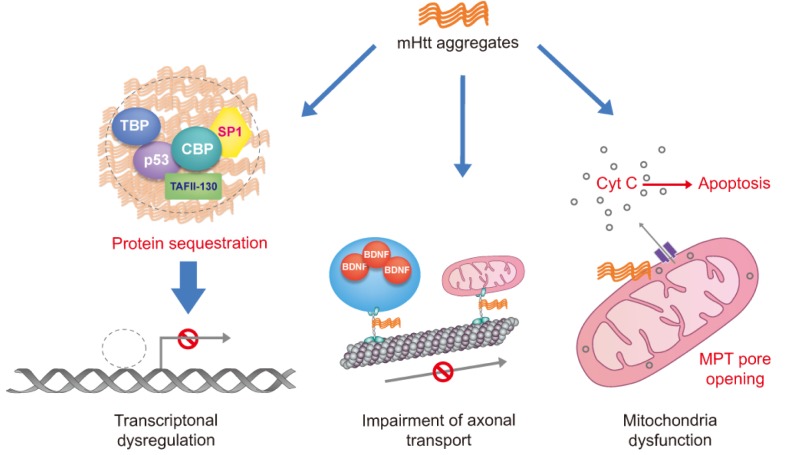
Fig. 1.
Potential molecular pathogenesis of toxicity of mHtt aggregates. Mutant huntingtin may affect the aberrant interaction with or sequester transcription factors leading to transcriptional dysregulation of many genes. Moreover, mutant huntingtin causes defects in trafficking of vesicle and cellular organelle such as mitochondria through long dendritic and axonal projections by affecting both molecular motors and microtubules. Finally, mutant huntingtin directly influence to decrease the Ca2+ threshold for MPT pore opening by interaction with the outer mitochondrial membrane, leading to Cyt c release and apoptosis. Mutant huntingtin (mHtt), cAMP response element binding protein (CREB) binding protein (CBP), TATA-binding protein (TBP), specificity protein 1 (SP1) and TBP-associated factor, 135 kDa (TAFII-130), brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), mitochondrial permeability transition (MPT), Cytochrome c (Cyt c).