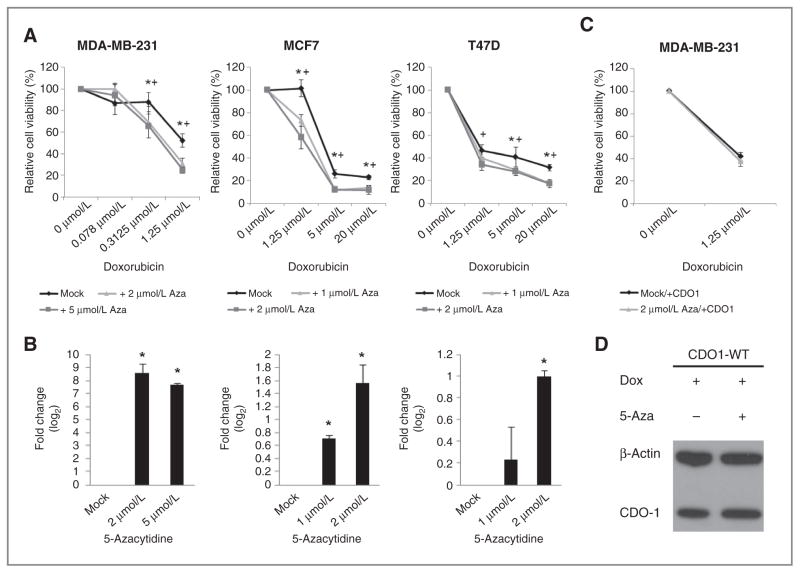
Figure 5.
Reactivation of epigenetically silenced CDO1 through priming with 5-azacytidine contributes to the sensitization of breast cancer cells to anthracycline treatment. A, cell viability of MDA-MB-231, MCF7, and T47-D cells primed with 5-azacytidine at doses ranging from 1 μmol/L to 5 μmol/L for 72 hours and subsequently treated with doxorubicin at doses ranging from 0.078 μmol/L to 20 μmol/L for 48 hours. Obtained values are plotted as % relative to doxorubicin-untreated cells. Group comparisons were carried out using Student t test. *, P < 0.05 for 1 μmol/L 5-azacytidine in MCF7 and T47-D cells or 2 μmol/L in MDA-MB-231 cells. +, P < 0.05 for 2 μmol/L 5-azacytidine in MCF7 and T47-D cells or 5 μmol/L in MDA-MB-231 cells. B, quantitative reexpression of CDO1 in 5-azacytidine (1 μmol/L, 2 μmol/L, or 5 μmol/L for 72 hours)-treated cells prior doxorubicin treatment is shown in fold change (log2) relative to mock-treated cells. Group comparisons were carried out using Student t test. *, P < 0.05. C, cell viability of doxycycline-induced CDO1-stable MDA-MB-231 cells (doxycyline was supplemented every 24 hours throughout the entire experiment) primed with 5-azacytidine at a dose of 2 μmol/L for 72 hours and subsequently treated with doxorubicin at a dose of 1.25 μmol/L for 48 hours. Obtained values are plotted as % relative to doxorubicin-untreated cells. As a control, cell viability was measured in CDO1-stable MDA-MB-231 cells that were not treated with 5-azacytidine. D, restoration of CDO1 protein expression in MDA-MB-231 cells 72 hours posttreatment with doxycycline and with or without 5-azacytidine was confirmed by Western blot using α-CDO1 antibody and α-β-actin as a control.