Figure 1.
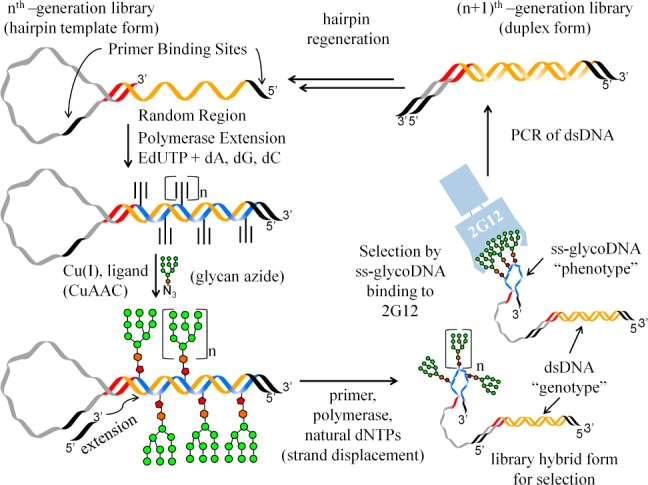
Overview of SELMA (SELection with Modified Aptamers). Selection begins with a library of DNA containing a template for the random sequence region (orange/blue section), flanked by primer binding sites and a hairpin structure terminating in a 3′ self-complementary patch of sequence. Polymerase extension with alkynyl base EdUTP substituted for TTP results in alkyne incorporation in the random region across from A’s in the template. A click reaction with glycan azide positions glycans across from A’s in the template, and then a primer is annealed inside the hairpin and extended with all natural dNTPs, displacing the glycosylated strand. The glycosylated ssDNA strand then folds in a sequence dependent manner, and the dsDNA region contains a copy of the same sequence as “natural” DNA, available for PCR. After selection by binding to immobilized target, the dsDNA of winning sequences is amplified, the hairpin section is rebuilt (not pictured), and the process is repeated.
