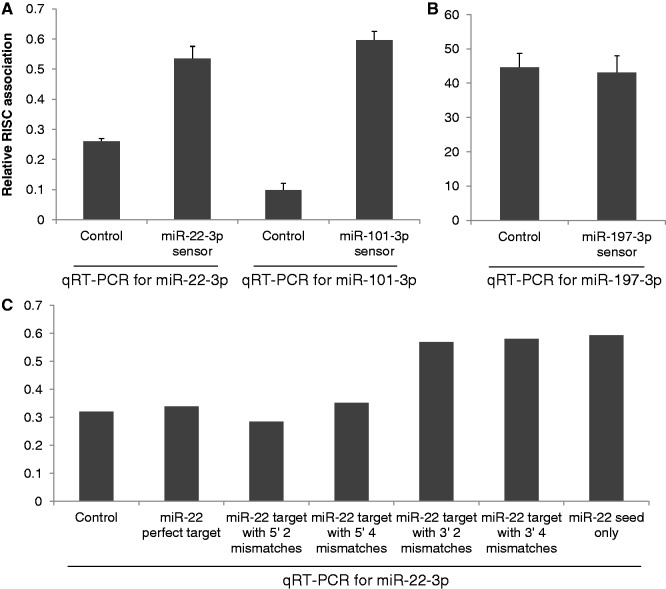
Figure 5.
Overexpression of a highly complementary miRNA target can enhance RISC association. (A) 293 cells were transfected with sensor constructs containing three copies of a predicted full-length miRNA target site bearing a bulge opposite miRNA nucleotides 10 and 11, or a control construct containing no inserted targets. Three days post-transfection, cells were collected and total small RNAs (≤200 nt), and RISC-associated, RNAs isolated. The indicated qRT-PCR analysis of miR-22-3p and miR-101-3p expression levels was normalized to miR-138, which does not show differential RISC association. The observed contribution of each miRNA relative to the RISC-associated miRNA pool is given relative to its contribution to the total miRNA pool, which was set at 1.0. Average of three independent experiments with s.d. indicated. (B) Similar to A, except that miR-197, which is highly RISC-associated, was analysed. (C) Similar to A, except that the sensor constructs used contained three perfect, fully complementary targets for miR-22-3p; three targets bearing mismatches opposite miRNA 5′ positions 1 and 2, three targets bearing mismatches opposite miRNA 5′ positions 1,2,3 and 4, three targets bearing mismatches opposite miRNA 3′ positions 21 and 22; three targets bearing mismatches opposite miRNA 3′ positions 19, 20, 21 and 22; or three targets showing only seed homology (nt 1–8) to miR-22-3p. Total and RISC-associated miRNA levels were analysed by qRT-PCR at 72 h post-transfection and are plotted as indicated in A.