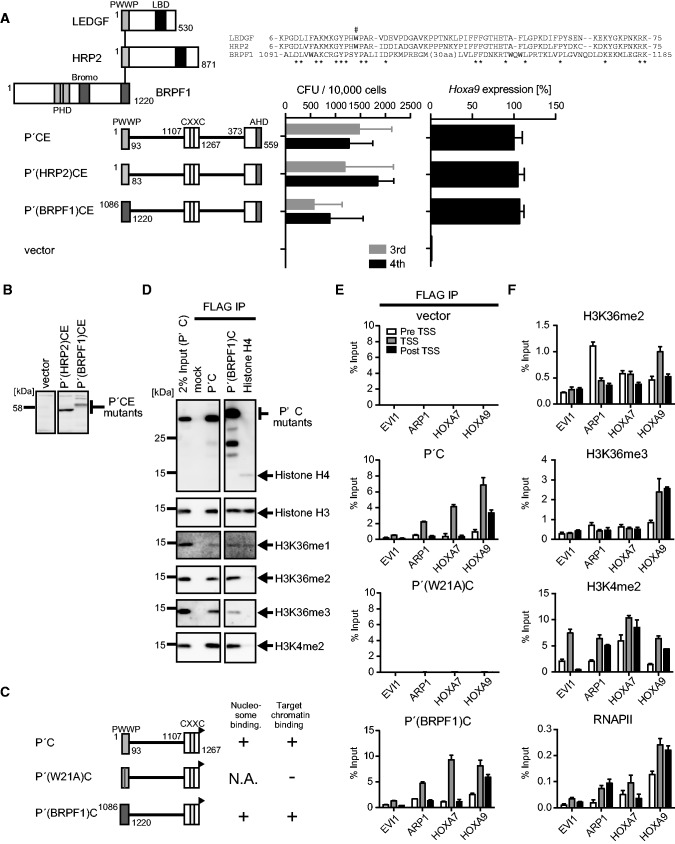
Figure 3.
The PWWP domain and the CXXC domain target active promoters containing H3K36me2/3 in vivo. (A) Transforming ability of P′CE mutants containing three different PWWP domains. The schematic structures of LEDGF, HRP2, BRPF1 and various P′CE mutants are shown (left). Sequence alignment of the three PWWP domains is shown. Asterisk, conserved residue. The tryptophan residue mutated in Figure 2A is indicated by #. The CFUs at the third and fourth rounds of replating are shown with error bars (SD of >3 independent experiments) (middle). Hoxa9 expression in the first-round colonies is expressed relative to that of P′CE (arbitrarily set at 100%) with error bars (SD of triplicate PCRs) (right). (B) Protein expression of the P′CE mutants carrying non-LEDGF PWWP domains in the packaging cells. The P′CE mutant proteins were visualized using the anti-ENL antibody. (C) The schematic structures of various P′C mutants. A FLAG tag (black flag) is fused to the C-terminal end of the P′C mutants. Their abilities to bind nucleosomes and target promoters are summarized. (D) Nucleosomes associated with the P′C mutants. The P′C mutants and their associating nucleosomes were co-purified by co-IP using the anti-FLAG antibody from the NUC fraction of 293T cells transiently expressing the P′C mutants. Nucleosomes were visualized by antibodies specific for histone H3 or the indicated modifications. Nucleosomes co-purified with FLAG-tagged histone H4 were also analyzed for comparison. (E) Chromatin targeting ability of the P′C mutants. Genomic localization of the P′C mutants was analyzed by ChIP using the anti-FLAG antibody in 293T cells transiently expressing the P′C mutants. The precipitated DNAs were analyzed by qPCR using specific probes for pre-TSS (−1.0 to −0.5 kb of TSS), TSS (0 to +0.5 kb of TSS) and post-TSS (+1.0 to 1.5 kb of TSS) of the indicated genes. (F) Epigenetic status of MLL target genes in 293T cells. ChIP analysis was performed on 293T cells using antibodies specific for H3K36me2, H3K36me3, H3K4me2 and RNAPII. The precipitated DNAs were analyzed by qPCR as in (E).