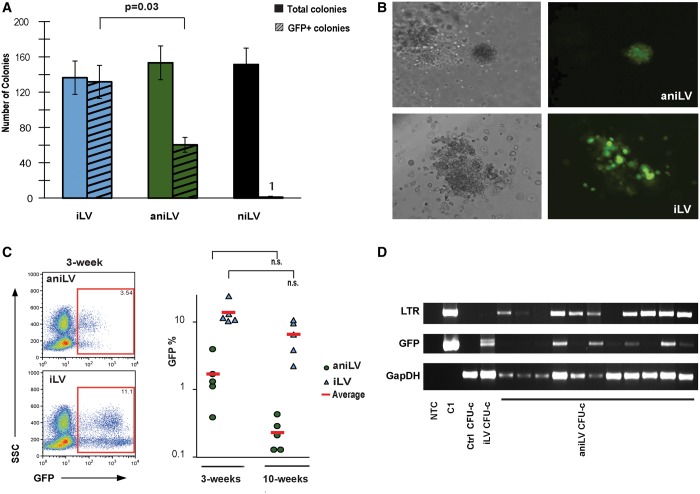
Figure 5.
LV transduction into murine HPC in vitro and in vivo. (A) Colony-forming assay of LV-transduced mHPCs in cytokine-supplemented methylcellulose. GFP expression from the colonies was analyzed at 10–12 days after transduction. Total number and GFP-positive colonies were counted. (B) Microscopic images of GFP expression from iLV and aniLV-transduced mHPC-derived colonies. Lower GFP expression was observed in aniLV compared with iLV-transduced colonies. (C) GFP expression profile in aniLV-transduced mHPC-transplanted animals. Each cohort represents five animals that received aniLV-transduced mHPCs. Representative FACS analysis of whole-blood cell sample of post-transduction and transplantation of mHPCs into the mice at 3 and 10 weeks, respectively. Lower MOI was consistent with CFU assay and 293T aniLV clones compared with cells transduced with iLV. (D) PCR analysis to detect the presence of episomal vector DNA in the vector-transduced CFUs. LTR junction amplification using PPT-F and PBS-R primers from aniLV CFUs suggests that colonies still harbor vector episomes at detectable levels. GFP PCR as vector control and murine-specific GapDH PCR to confirm the presence of genomic DNA in positive control sample and in untransduced control CFU-c.