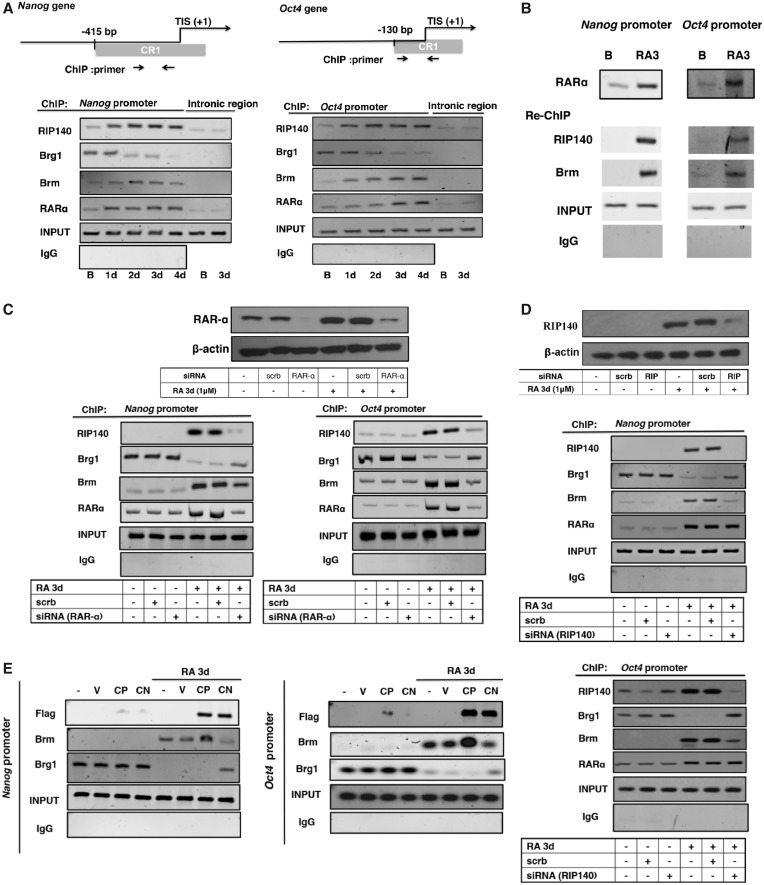
Figure 3.
RAR-α is involved in RIP140/Brm repressive complex in RA-induced ESC differentiation. (A) ChIP assay examining the kinetics of RIP140, Brm, Brg1 and RAR-α recruitment on the promoters of Nanog or Oct4 genes. Primers specific to the introns of Nanog and Oct4 were used for negative controls. The positions of primer pairs are depicted on the map. (B) Re-ChIP to monitor endogenous RAR-α associated with RIP140 and Brm on Nanog or Oct4 gene promoter on day 3 of RA treatment. (C) Upper: WB showing the expression of RAR-α in ESCs transfected with scrb siRNA or RAR-α siRNA. Lower: ESCs were transfected with scrb or siRNA specific to RAR-α, and then were treated with RA for 72 h after 6 days of siRNA transfection. ChIP assay was conducted to examine the recruitment of Brm, Brg1, RAR-α and RIP140 on the promoters. (D) Upper: WB showing the expression of RIP140 in ESCs transfected with scrb siRNA or RIP140 siRNA. Lower: RIP140 is required for Brm/Brg1 exchange. ESCs were transfected with scrb or siRNA specific to RIP140, treated with RA for 72 h after 6 days of siRNA transfection. ChIP assay was conducted to examine the recruitment of Brm, Brg1, RAR-α and RIP140 on the promoters. (E) RIP140 lysine acetylation is important for Brm/Brg1 exchange. ESCs were treated with control (empty vector), CN or CP, then treated with RA for 72 h. ChIP assay was conducted to examine the Brm, Brg1 and RIP140 recruitment to the promoters of the Nanog or Oct4 genes.