Figure 3.
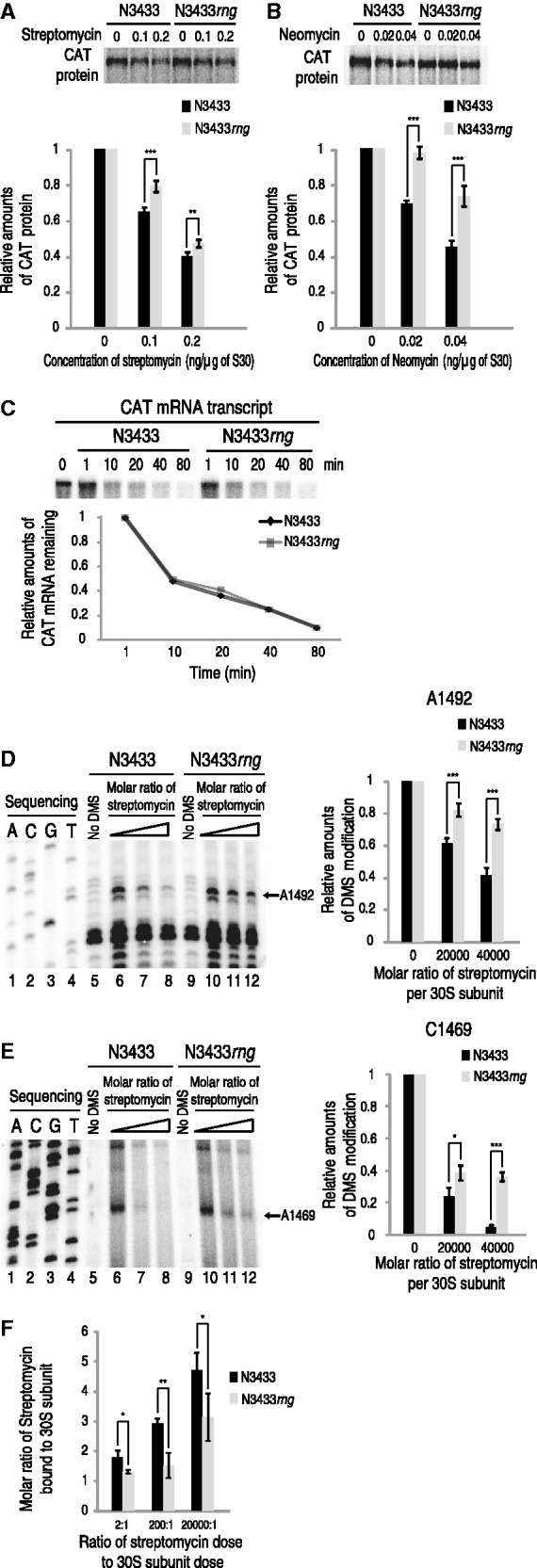
Effects of 16S+3∼7 accumulation on the sensitivity and binding capacity of ribosomes to aminoglycosides. (A and B) Effects of 16S+3∼7 accumulation on the sensitivity of ribosomes to aminoglycosides. In vitro translation was performed for CAT protein production using in vitro-synthesized CAT transcripts in the presence of streptomycin (A) or neomycin (B). Cell-free translation reactions were performed using S30 extracts prepared from N3433 and N433rng cells in addition to CAT mRNA. The protein samples were analyzed by 12% SDS-PAGE, and CAT protein production was detected using a phosphorimager. (C) The stability of CAT mRNA transcripts during in vitro translation. Cell-free translation reactions similar to those described above were performed using CAT mRNA transcripts uniformly labeled with [γ-32P]ATP. Samples were obtained after 1, 10, 20, 40 and 80 min of reaction time. The RNA transcripts were purified and analyzed on an 8% polyacrylamide gel containing 8 M urea. (D and E) Chemical probing of the 3' minor domain within the 16S rRNA with DMS in the presence of streptomycin. Chemical protection assays with DMS were performed using 30S subunits purified from the 70S ribosomes of the N3433 and N3433rng strains. Lanes 1–4, dideoxy sequencing reactions; lanes 5 and 9, control extension reaction with unmodified rRNA (no DMS); lanes 6 and 10, chemical probing in the absence of antibiotics; lanes 7, 8, 11 and 12, chemical probing with DMS in the presence of streptomycin at the molar ratio indicated. Reverse transcriptase stops at the position before a modified nucleotide; therefore, the bands indicate a modification at the next base in the sequence. (F) Molecular ratios of streptomycin bound to 30S subunits extracted from N3433 and N3433rng strains. 30S subunit sample (each 0.015 nmol dose) treated with a dose of streptomycin at 0.03, 3 and 300 nmol was analyzed by mass spectrometry as described in Materials and methods and Supplementary Figure S6.
