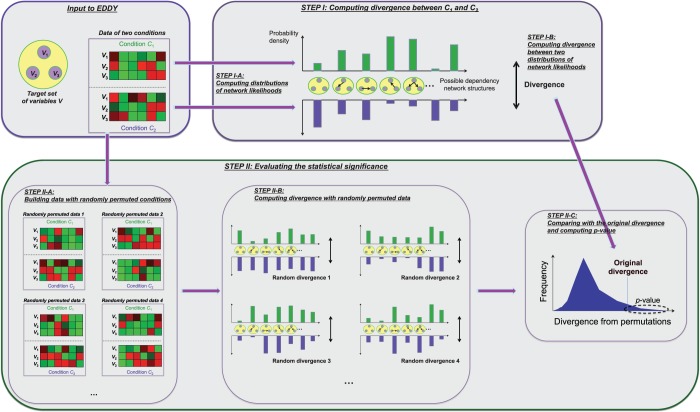
Figure 1.
The conceptual outline of EDDY. A target gene set and gene expression data of two conditions C1 and C2 are given as input. (STEP I-A) The probability distribution of dependency network likelihood is computed for each condition. (STEP I-B) The divergence between C1 and C2 is computed from the two probability distributions of dependency network likelihoods. (STEP II-A) Random data sets are built by shuffling sample condition labels. (STEP II-B) For each random data set, a random divergence is computed. The collection of all random divergences constitutes the null distribution of divergence. (STEP II-C) The P-value of the original divergence is evaluated in comparison with the computed null distribution of divergence.