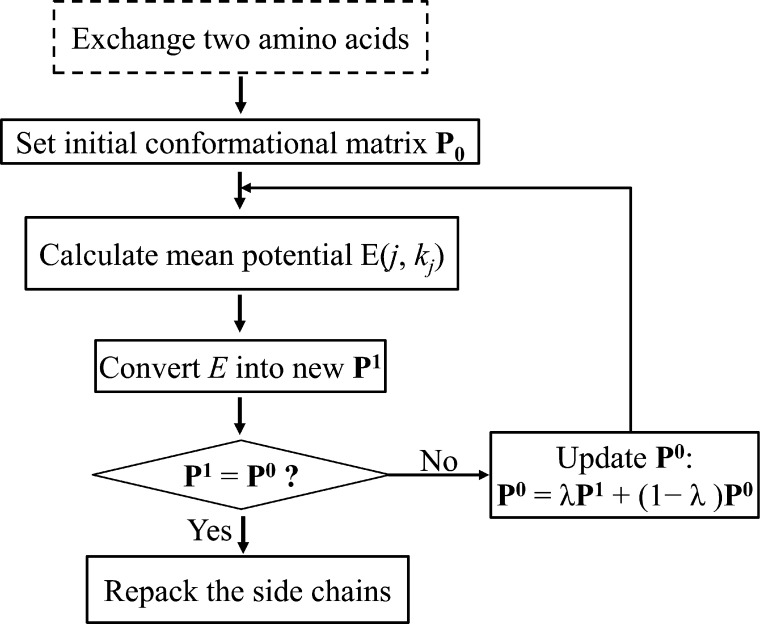
Figure 3.
Self-consistent mean field (SCMF) procedure. A trial exchange between two amino acids is implemented. The conformational probability matrix P0 is set initially so that all possible rotamers at any one site have equal probabilities. The effective potential experienced by each rotamer at each site is calculated, and the Boltzmann law is used to determine new conformational probabilities of the rotamers for each amino acid and hence a new conformational probability matrix P1. If the absolute error between P0 and P1 is less than 10–3, the rotamer combination with the highest conformational probability is selected from P1 to repack the side chains. Otherwise, the conformational matrix P is updated by employing a self-consistent iteration until the absolute error falls below a certain tolerance.