Figure 5.
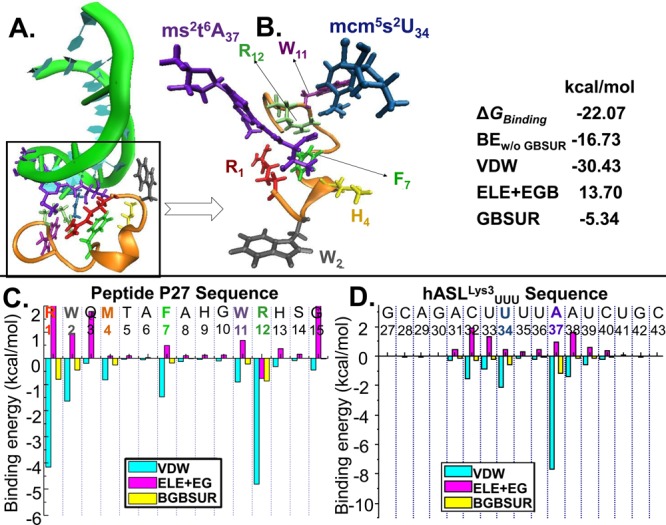
Peptide P27 binds the modified hASLLys3UUU with high affinity and specificity. (A) The computed equilibrium binding structure of the modified hASLLys3UUU bound by P27. The peptide backbone is in gold, and the ribose-phosphodiester backbone of the hASLLys3UUU is colored in green. (B) Enlargement of the interaction demonstrating the specificity achieved in the binding of the two modifications by the amino acids R1 (red), F7 (light green), W11 (light purple), and R12 (dark green). The peptide backbone is in gold and the side chains in color. The modifications ms2t6A37 (purple) and mcm5s2U34 (blue) are bound by amino acids at the beginning, middle, and end of the peptide. The ribose-phosphodiester backbone of the hASLLys3UUU is not shown. The table characterizes the contributions of different binding modes: ΔGBinding, Gibbs free energy of binding; BEw/o GBSUR, binding energy without GBSUR; VDW, van der Waals energy; ELE, electrostatic energy; EGB, polar solvation energy based on the generalized Born (implicit solvent) model; and GBSUR, nonpolar solvation energy, which is the product of the solvent-accessible surface area of the solute molecules and the interfacial tension between the solute and solvent. (C) Individual contributions of each amino acid to the VDW, ELE + EGB, and GBSUR. The amino acids are colored as in B. (D) Individual contributions of each nucleoside to the VDW, ELE + EGB, and GBSUR. The nucleosides engaged in the interaction with P27 are those of the anticodon loop, particularly the modified nucleosides at U34 and A37. The modified nucleosides are colored as in B.
