Figure 1.
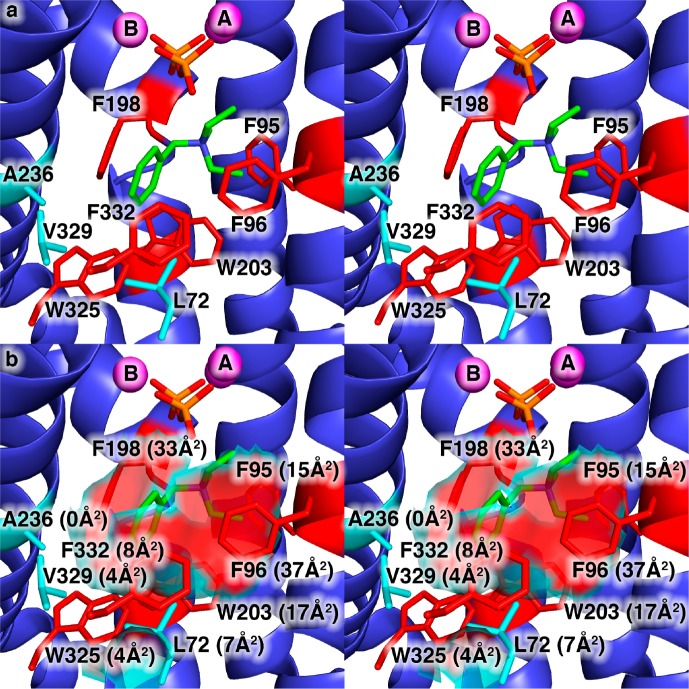
(a) View of the hydrophobic EIZS active site in the wild-type EIZS–Mg2+3–PPi–BTAC complex showing the locations of aromatic residues (red) and aliphatic residues (cyan) that largely define the active site contour shown in panel b. Portions of the protein structure in the foreground, including the α-helix containing W325, V329, and F332, are cut away to allow the active site to be viewed. Mg2+ ions are shown as magenta spheres. P and O atoms of the PPi anion are colored orange and red, respectively. C and N atoms of the BTAC cation are colored green and blue, respectively. The solvent-accessible surface area contributed by each residue is given in parentheses. Note that although A236 does not contribute to the solvent-accessible surface area in the wild-type enzyme, it is sufficiently close to the surface that substitution of larger side chains will impact the surface contour.